Figure 4.
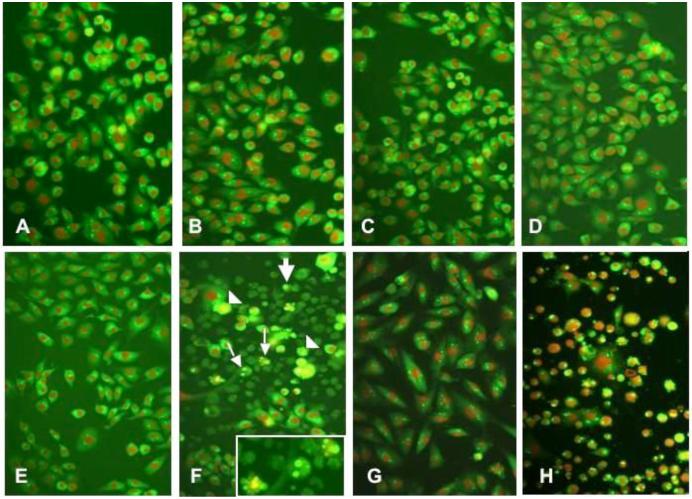
Glioma cells shown by fluorescence microscopy after undergoing a morphologic assay for apoptosis by the acrid ine orange/ethidium bromide staining. The cells shown were incubated under the following control or experimental conditions: (A) nontransfected U-251MG cells, (B) nontransfected U-251MG cells + FasL (C) U-251MG cells transfected with siRNA luc, (D) U-251MG cells transfected with siRNA luc + FasL, (E) U-251MG cells transfected with siRNA PATZ1, (F) U-251MG cells transfected with PATZ1 siRNA + FasL, (G) U-373MG cells transfected with PATZ1 siRNA + FasL, and (H) U-87MG cells transfected with PATZ1 siRNA + FasL. In panels F and H, a large number of glioma cells are seen with morphologic changes indicative of a poptosis that include cells with nuclear fragmentation (small arrows), membrane blebbing (arrowheads), and small cells with condensed nuclei (large arrows). In F, the inset shows three cells at a higher magnification where nuclear fragmentation is occurring.
