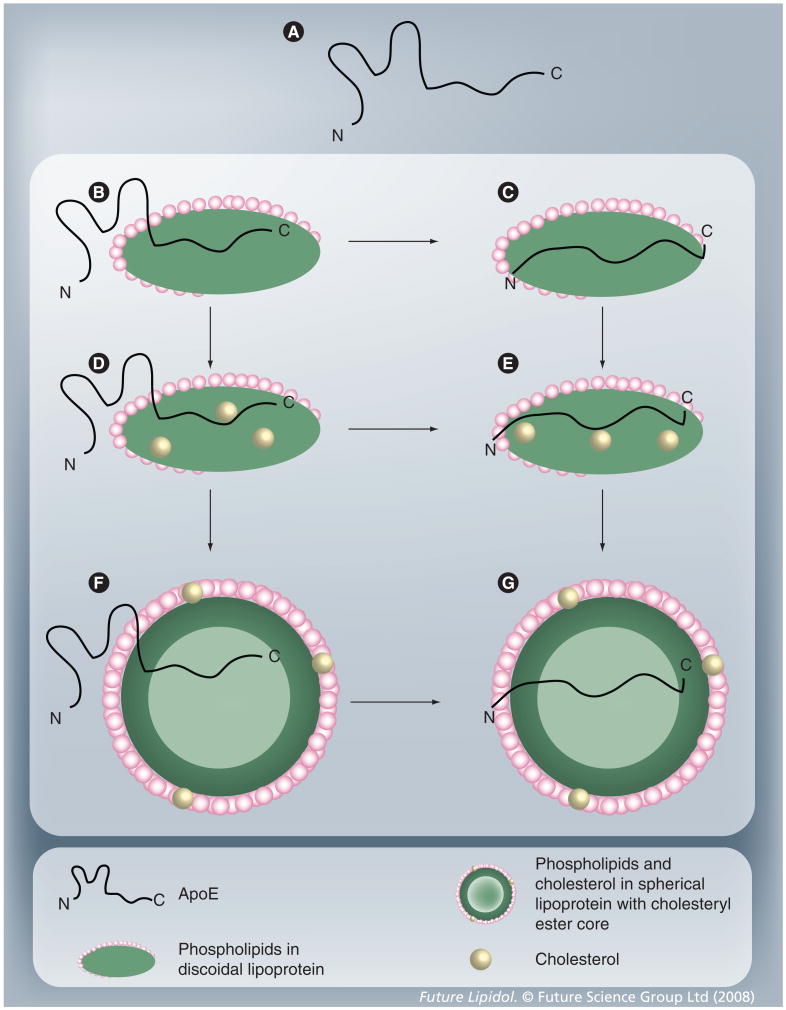
Figure 5. Conformational adaptability of ApoE.
(A) Lipid-free ApoE; (B and C) ApoE bound to discoidal phospholipid particles, with the N-terminal domain remaining unbound (B) or bound to lipids (C); (D and E) ApoE bound to discoidal phospholipid and cholesterol-containing particles, with the N-terminal domain remaining unbound (D) or bound to lipids (E); (F and G) ApoE bound to spherical phospholipid particles with cholesteryl ester core, with the N-terminal domain remaining unbound (F) or bound to lipids (G). Since these are not discrete states, numerous intermediate conformational states of ApoE with different extents of lipidation are possible between states (A) and (G).