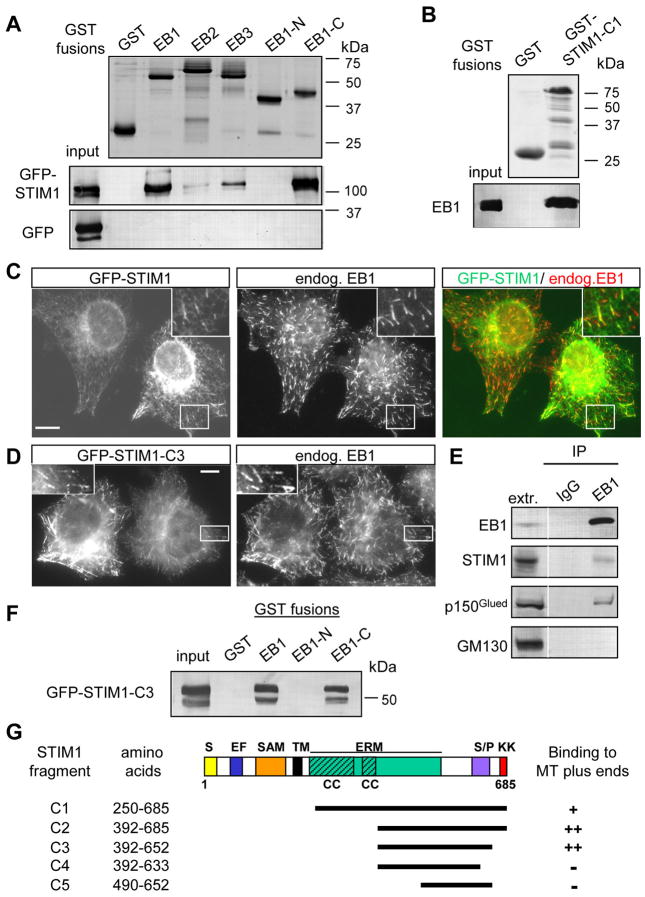
Figure 1. STIM1 interacts with EB1.
A,B,F. GST pull down assays with the indicated GST fusions; extracts of HEK293 cells overexpressing GFP-STIM1, GFP-STIM1-C3 mutant or GFP alone were used in A and F, and the purified full length EB1 protein in B. Coomassie-stained gels are shown for GST fusions; other proteins were detected by Western blotting with antibodies against GFP (A, F) or EB1 (B).
C, D. HeLa cells were transfected with GFP-STIM1 or GFP-STIM1-C3 mutant, fixed and stained for the endogenous EB1. The insets show enlargements of the boxed areas. In the overlay GFP-STIM1 is shown in green and EB1 in red. Bars, 10 μm.
E. Immunoprecipitation from extracts of HeLa cells with the rabbit polyclonal antibody against EB1 or a control rabbit serum. The lane marked “extr.” shows 5% of the input. Dynactin subunit p150Glued, a known EB1 partner, was used as a positive control, and GM130, a protein associated with the cytoplasmic side of the Golgi, as a negative control.
G. Mapping of the minimal MT plus end binding domain of STIM1 by colocalization with EB1 in fixed HeLa cells. A scheme of STIM1 protein structure and the deletion mutants is shown; S, signal peptide; EF, EF hand; SAM, sterile α motif domain; TM, transmembrane domain; ERM, ezrin-radixin-moesin domain; CC, coiled coil; S/P, serine-proline rich domain; KK, lysine-rich domain.