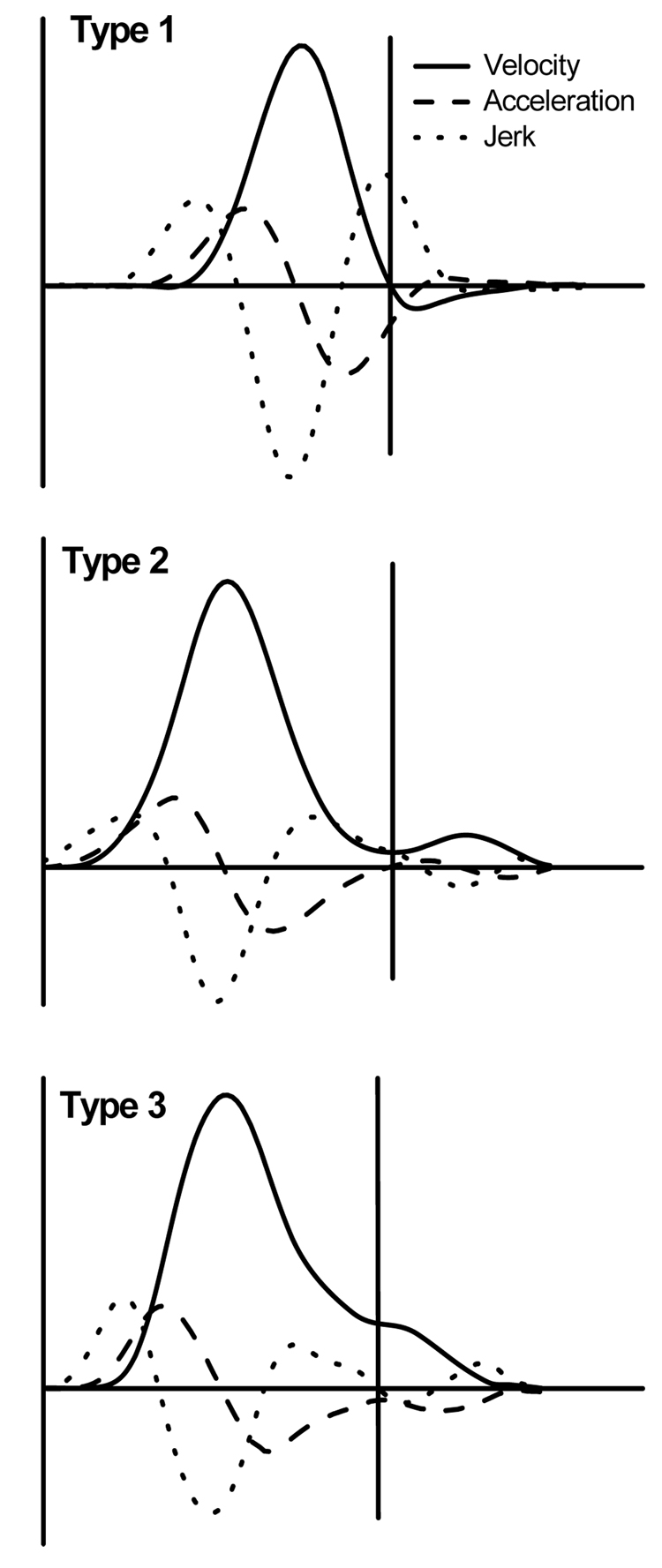
Figure 2.
Examples of discrete movements with secondary submovements of type 1, 2, and 3. The vertical line marks the end of the primary submovement and the beginning of the secondary submovement. Type 1 submovement emerged when the smooth primary submovement was interrupted by a velocity zero-crossing from positive to negative values. Type 2 submovement was characterized by an acceleration zero-crossing from negative to positive values. A jerk zero-crossing from positive to negative values was indicative of a type 3 submovement.