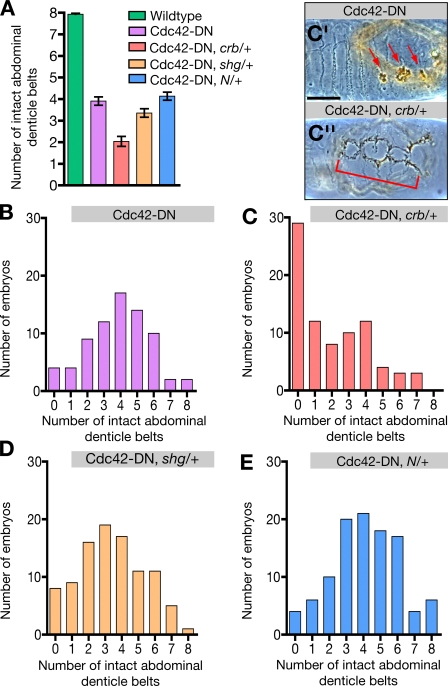
Figure 7.
crb and shg enhance the Cdc42-DN phenotype. Quantification of ventral cuticle defects in wild-type; Cdc42-DN; Cdc42-DN, crb/+; Cdc42-DN, shg/+; and Cdc42-DN, Notch/+ embryos. Embryo collections of double-mutant genotypes contained a predicted 50% of double mutants and 50% of Cdc42-DN embryos. (A) The number of intact abdominal denticle belts is presented as mean ± SEM (error bars). For Cdc42-DN, crb/+ and Cdc42-DN, shg/+ embryos, the difference in the mean number of intact belts relative to Cdc42-DN embryos is statistically significant (P < 0.001). For Cdc42-DN, Notch/+ embryos, there is no significant difference relative to Cdc42-DN embryos. (B) Distribution of ventral cuticle phenotypes in a population of Cdc42-DN embryos. (C) Distribution of ventral cuticle phenotypes in a population in which 50% of embryos are predicted to be Cdc42-DN and 50% are predicted to be Cdc42-DN, crb11a22/+. (C′) Ventral cuticle of a Cdc42-DN embryo. Arrows indicate holes in the ventral surface. (C′′) Ventral cuticle of an embryo from a Cdc42-DN, crb/+ population with severely enhanced ventral defects (indicated by bracket). (D) Distribution of ventral cuticle phenotypes in a population in which 50% of embryos are predicted to be Cdc42-DN and 50% are predicted to be Cdc42-DN, shgR69/+. (E) Distribution of ventral cuticle phenotypes in a population in which 50% of embryos are predicted to be Cdc42-DN and 50% are predicted to be Cdc42-DN, N55e11/+. Bar, 100 μm.