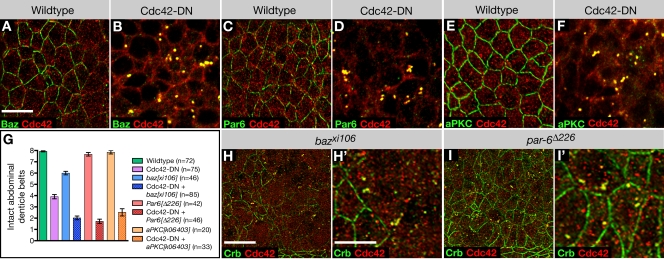
Figure 8.
Cdc42 interacts with the Par complex to regulate apical endocytosis. (A and B) Wild-type (A) and Cdc42-DN (B) embryos labeled for Baz and Cdc42. (C and D) Wild-type (C) and Cdc42-DN (D) embryos labeled for Par6 and Cdc42. (E and F) Wild-type (E) and Cdc42-DN (F) embryos labeled for aPKC and Cdc42. (G) Cdc42-DN ventral defects are enhanced by the loss of zygotic aPKC, baz, or par6. The extent of ventral cuticle defects was quantified by counting the number of intact abdominal denticle belts (mean ± SEM [error bars]). For all double-mutant combinations, the difference in the mean number of intact belts relative to Cdc42-DN embryos is statistically significant (P < 0.001). (H and I) baz mutant embryos (H and H′) and par6 mutant embryos (I and I′) labeled for Crb and Cdc42. Bars: (A–F, H′, and I′) 5 μm; (H and I) 10 μm.