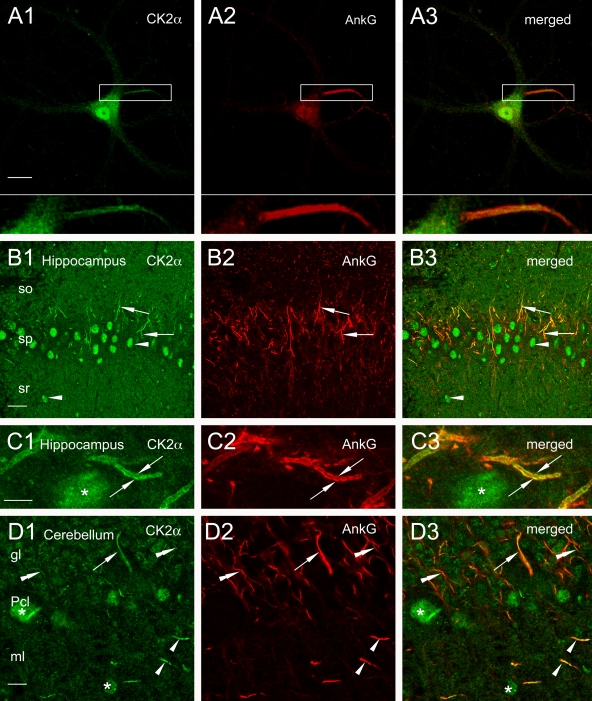
Figure 4.
CK2α is concentrated at AISs. (A) A cultured hippocampal neuron was immunostained for CK2α (A1) and ankyrin G (A2). CK2α immunoreactivity is highly expressed in the initial segment (box). Enlarged views of the initial segment are visualized in A1–A3, bottom. (B and C) In the CA1 area of the hippocampus, CK2α immunoreactivity is visible within nuclei (B1, arrowheads) of putative pyramidal cells and interneurons. As demonstrated by colabeling with ankyrin G (B2, arrows), CK2α is present in initial segments all over the different strati (B1 and B3, arrows). CK2α shows light and diffuse additional staining within the neuropil. CK2α immunoreactivity (C1 and C3, arrows) and ankyrin G labeling (C2, arrows) are concentrated along the cytoplasmic membrane of an initial segment in the stratum pyramidale next to a CK2α-labeled nucleus (C1 and C3, asterisks). (D) In cerebellum, nuclei (D1, asterisk) of Purkinje cells and interneurons of the molecular layer (ml) are labeled for CK2. Coimmunolabeling for CK2α (D1) and for ankyrin G (D2) is visible within initial segments of a putative Purkinje cell (D1–D3, arrows), granular cells (D1–D3, double arrowheads), and interneurons (D1–D3, single arrowheads). gl, granular layer; Pcl, Purkinje cell layer, so, stratum; sp, stratum pyramidale; sr, stratum radiatum. Bars: (A) 23 μm; (B) 26.8 μm; (C and D) 6.82 μm.