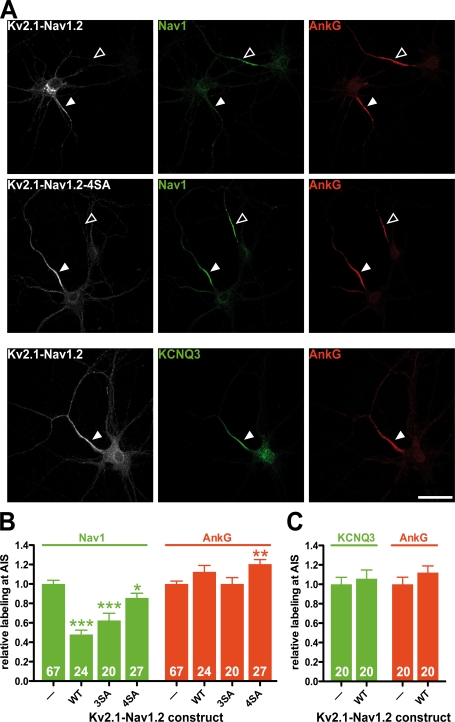
Figure 6.
Impact of Kv2.1-Nav1.2 and of phosphorylation-deficient Kv2.1-Nav1.2 constructs on the accumulation of sodium channels (Nav1) and KCNQ2/KCNQ3 potassium channels at the AIS of cultured hippocampal neurons. (A, top and middle) Kv2.1-Nav1.2 expression perturbed Nav1 accumulation at the AIS, unlike the phosphorylation-deficient Kv2.1-Nav1.2 4SA mutant. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with either Kv2.1-Nav1.2 or phosphorylation-deficient Kv2.1-Nav1.2 mutants. Then cells were stained for myc (gray), ankyrin G (red), and sodium channels (green). (B) Quantification of Nav1 and ankyrin G staining intensity in untransfected cells (A, open arrowheads) and in transfected cells (closed arrowheads). (A, bottom) Kv2.1-Nav1.2 expression did not perturb KCNQ3 accumulation at the AIS. Cells transfected with Kv2.1-Nav1.2 were subsequently stained for myc (gray), ankyrin G (red), and KCNQ3 potassium channels (green). (C) Quantification of KCNQ3 and ankyrin G staining intensity. Fluorescence intensity measured in transfected cells, identified by myc staining, was normalized by taking as 100% the staining intensity measured in nontransfected cells (arrowheads). Numbers at the base of the bars denote the number of quantified cells. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Mann-Whitney test: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. WT, wild type. Bars, 10 μm.