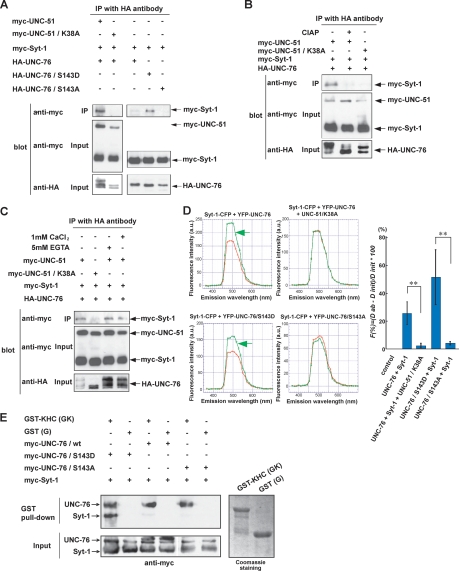
Figure 6.
UNC-51 regulates the affinity between UNC-76 and Syt-1. (A) UNC-51-mediated association of Syt-1 and UNC-76. Myc- or HA-tagged UNC-51 (full-length), UNC-76 (full-length), and Syt-1 (full-length) were coexpressed in HEK293T cells as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA followed by immunoblot with anti-myc. (B) Phosphorylation-dependent association of Syt-1 and UNC-76. HA-UNC-76, myc-Syt-1, and myc-UNC-51 or UNC-51/K38A were expressed in HEK293T cells as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA. The immunecomplexes were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-myc. (C) Syt-1–UNC-76 interaction does not require Ca2+. HA-UNC-76, myc-Syt-1, and myc-UNC-51 or UNC-51/K38A were expressed in HEK293T cells as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA. The immune complexes were incubated in the presence of EGTA or CaCl2 and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-myc. (D) Syt-1–UNC-76 interaction detected by FRET. COS7 cells were transfected with Syt-1-CFP, YFP-UNC-76, YFP-UNC-76/S143D, YFP-UNC-76/S143A, or UNC-51/K38A in combination as indicated. For each combination, initial (red) and fluorescence after acceptor photobleaching spectra (green) were plotted for a range of wavelengths indicated. Increase in donor fluorescence after acceptor bleaching indicates FRET (green arrows). Quantification of FRET (graph). (**) Statistical significance (P < 0.01). (E) KHC/UNC-76/Syt-1 complex formation. GST alone (G) and GST fused with KHC (amino acids 675–975) (GK) were produced in E. coli, purified on Glutathione-Sepharose beads, and incubated with myc-UNC-76 and myc-Syt-1 expressed in HEK293T cells. Proteins that bound to the beads were eluted and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-myc.