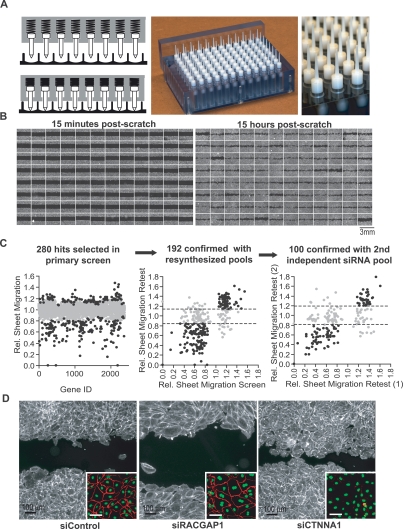
Figure 2.
Design, implementation, and validation of a 96-well formatted assay for sheet migration. (A) High throughput scratch tool with 96 individual spring loaded tips capable of generating uniform cell-free bands in a multiwell format. (Left panel) Diagrams of spring loaded tips with and without applied pressure. (Middle and right panels) Photographs of the scratch unit and the tips, respectively. (B) Montages of 96 images from a multiwell plate where each well was transfected with a different pool of siRNA. Fluorescent images were taken 15 min (left panel) and 15 h (right panel) after cell removal. (C) Results from siRNA screens targeting 2400 human signaling proteins. (Left panel) Sheet migration rates (gray dots) are the mean of duplicates and normalized to plate medians. A subset of genes (black dots) was selected for retest based on their deviation from median. (Middle panel) As a control, pools of siRNAs were resynthesized and retested. (Right panel) As a second control, repeating hits (black dots) were again selected and a second, independent siRNA pool was synthesized against the same targets and retested. One-hundred hits that showed consistent deviations in all experiments were considered confirmed hits. For both retest experiments, sheet migration rates were normalized to cells transfected with control siRNA, and each retest experiment was performed at least four times. (D) Examples of siRNA effects on sheet migration. Cells transfected with control, RACGAP1 and CTNNA1 siRNAs, were stained with fluorescein-phalloidin (main image) and VE-cadherin (inset).