Fig. 1.
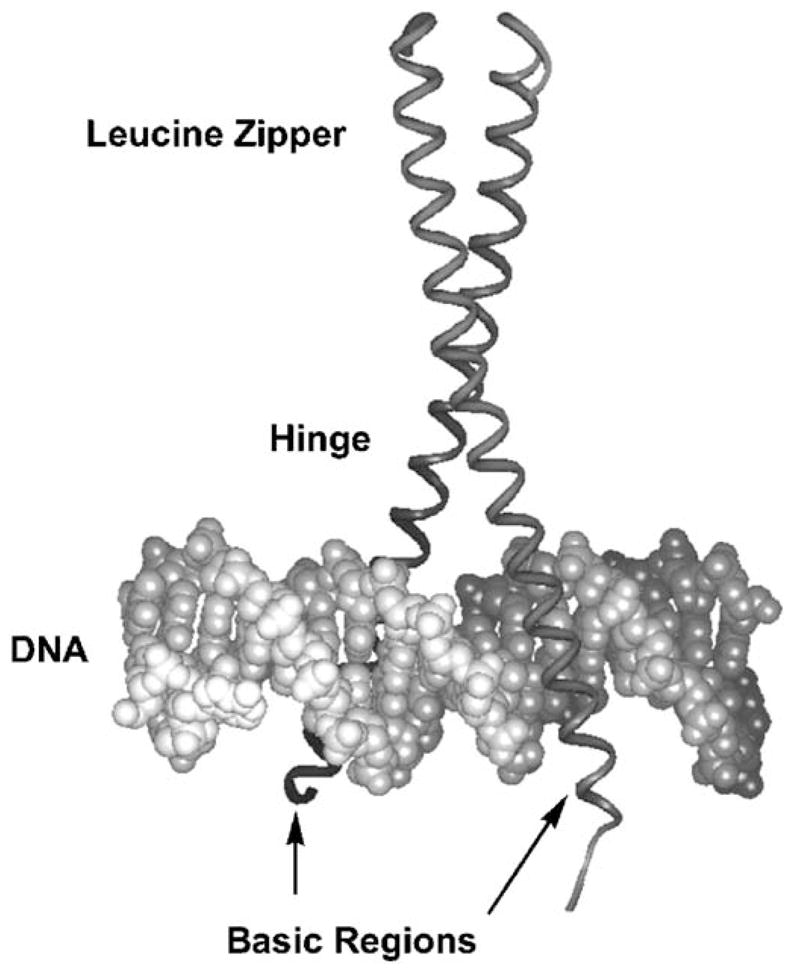
GCN4 bZIP in complex with the AP-1 DNA site [3]. DNA is the double helix at the bottom of the figure, and the bZIP is the vertical ribbon, α-helical dimer. The leucine zipper dimerizes into the coiled-coil structure shown at the top of the figure; the zipper then smoothly forks to either side of the DNA (hinge region), thus allowing the basic region dimer to bind opposite sides of the DNA major groove.
