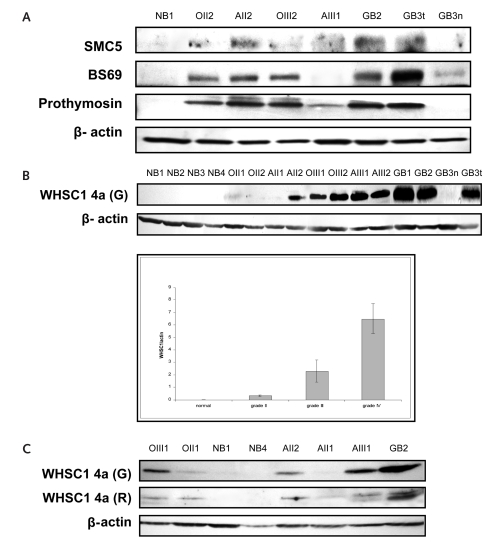
Fig. 1.
Proteomic findings are validated by Western blot. The specimens included four normal brain tissues (NB1–NB4); tissues from oligodendroglioma grade II (OII1, OII2) and grade III (OIII1, OIII2), astrocytoma grade II (AII1, AII2) and grade III (AIII1, AIII2), and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM; GB1–GB4); and tissues from a microdissected normal region (GB3n) and tumor (GB3t), both from the same GBM patient. (A) SMC5, BS69, and prothymosin are absent in normal brain tissue and are expressed at varied levels in gliomas. (B) Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1 (WHSC1) isoform 4a protein expression is correlated with the malignancy of gliomas. Polyclonal anti-WHSC1 antibody raised from goat recognized a single immunoblotting signal at 30 kDa from all brain tumor tissues (upper panel). The immunosignal was completely absent in normal brain and in normal brain tissue from the microdissected GBM. The blotting signal density was higher in GBMs than in grade III tumors and was higher in grade III than in grade II tumors. As a loading control, 42-kDa β-actin protein was detected from the same blotting membrane after stripping out WHSC1 4a immunosignals. The lower panel summarizes the densitometry results of the WHSC1 4a expression. (C) The WHSC1 4a protein expression was reconfirmed by Western blotting by using another polyclonal anti-WHSC1 antibody that was recently developed from rabbit. Both antibodies identified a consistent pattern of WHSC1 expression.