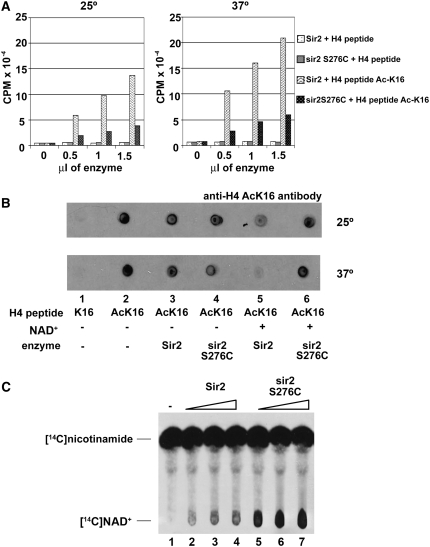
Figure 6.—
Enzymatic assays with recombinant Sir2 and sir2 S276C. (A) NAD+ hydrolysis. Assays were performed by incubating enzyme (0–1.5 μl of Sir2 or sir2 S276C, 100 ng/μl), radioactive NAD+ labeled on the nicotinamide moiety, and H4 peptide (unacetylated or acetyl-K16) at 25° or 37° for 1 hr. Activity was determined by measuring the amount of [3H]nicotinamide released. The sir2 S276C mutant protein shows defective NAD+ hydrolysis activity at both temperatures. (B) Deacetylase assays. The assays were performed by incubating enzyme (100 ng of Sir2 or sir2 S276C), +/− NAD+, and H4 peptide (unacetylated or acetyl-K16) at 25° or 37° for 1 hr. The reaction mixture was spotted onto paper and activity was determined by probing with an anti-H4 acetyl-K16 antibody. Deacetylase activity is shown by a weaker response to the H4 acetyl-K16 antibody. As in A, sir2 S276C shows defective deacetylase activity at both temperatures. (C) NAD+–nicotinamide exchange assays. The assays were performed by incubating enzyme (2–6 μl of Sir2 or sir2 S276C, 100 ng/μl), NAD+, radioactive nicotinamide and chicken histones at 30° for 1 hr. Activity was determined by the amount of [14C]NAD+ formed. sir2 S276C protein shows enhanced NAD+–nicotinamide exchange activity compared with Sir2.