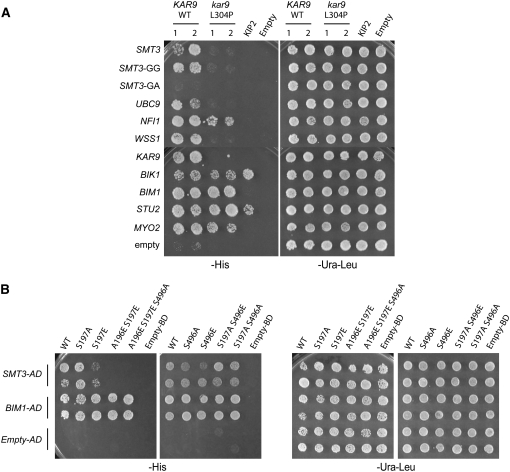
Figure 6.—
(A) The kar9-L304P mutation disrupts interactions with sumoylation proteins, but not with microtubule-associated proteins or Myo2p. AD-SMT3, AD-SMT3-GG, AD-SMT3-GA, AD-UBC9, AD-NFI1, AD-WSS1, AD-KAR9 (aa 1–393) (pRM1895), AD-BIK1 (pRM2627), AD-BIM1 (pRM1893), AD-STU2 (aa 649–888) (pRM1916), and AD-MYO2 (aa 1083–1574) (pRM2473) or empty AD was transformed into the two-hybrid reporter strain (yRM1756/PJ69-4α) and selected on media lacking leucine. KAR9-BD or kar9-L304P-BD was transformed into the two-hybrid reporter strain with the opposite mating type (yRM1757/PJ69-4A) and selected on media minus uracil. After mating, diploids were selected on media lacking uracil and leucine (−ura −leu). Two colonies containing either wild-type KAR9 or kar9-L304P were analyzed. Growth was scored on plates lacking histidine (−his) at 30° after 2–3 days. (B) Phosphorylation of Kar9p at serine 197 inhibits the interaction between KAR9 and SMT3. Phospho-mimetic and phospho-inhibitory mutants of Kar9p were generated in which serine 197 and/or serine 496 were mutated to alanine (A) or glutamic acid (E) by site-directed mutagenesis (Moore and Miller 2007). GAL4-DNA binding domain fusions of these mutants were tested against the activation domain fusions of SMT3 and BIM1 in a two-hybrid reporter strain lacking BIM1 (yRM2057) by scoring growth on media lacking histidine (−his) after incubation at 30° for 2–3 days. The following strains containing BD fusions were used: kar9-S197A (pRM6050), kar9-S197E (pRM5617), kar9-A196E S197E (pRM6255), kar9-A196E S197E S496A (pRM6295), kar9-S496A (pRM5777), kar9-S496E (pRM5619), kar9-S197A S496E (pRM6294), and kar9-S197A S496A (pRM6113). The A196E S197E mutant disrupts the interaction between KAR9 and SMT3, but not with BIM1.