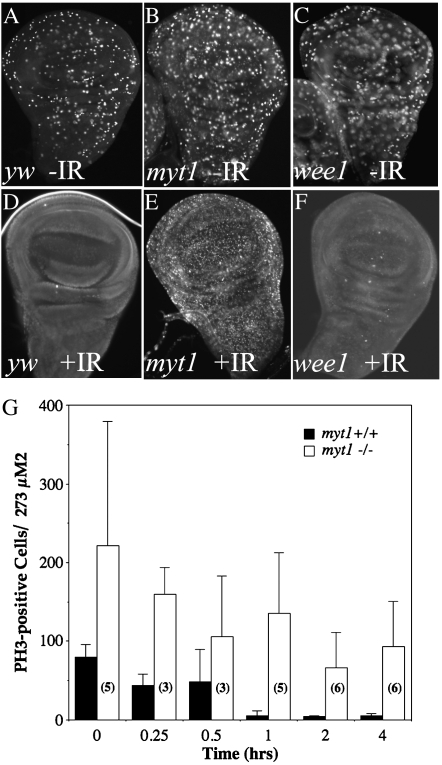
Figure 4.—
myt1 mutants are defective for normal cellular responses to ionizing radiation. Wing imaginal discs were dissected from wandering third instar larvae that had been immunolabeled with antibodies against phospho-histone H3 as a marker for mitotic cells. Comparisons of unirradiated and irradiated wing discs are shown for each of the following genotypes: yw controls (A and D), myt11/myt11 mutants (B and E), and wee1ES1/Df(2L)weeWO5 mutants (C and F). The irradiated (IR) larvae were dissected 60 min after exposure to 40 Gy of ionizing radiation, in D–F. PH3-positive cells were seen in all of the unirradiated controls: yw (A), homozygous viable myt11 mutants (B), and wee1 mutant discs (C). There were almost no PH3-positive cells remaining in yw control discs or in wee1 mutant discs by 60 min after exposure to IR (D and F), indicating the presence of a functional premitotic checkpoint in these genotypes. In myt1 mutant discs (E) the PH3 antibody labeling persisted after IR exposure, suggesting a checkpoint defect. To quantify this defect, we counted the numbers of PH3-positive cells in yw control and myt1 mutant wing discs at intervals after exposure to ionizing radiation (G). The numbers (3–6) shown for each open bar indicate the number of control and mutant discs that were analyzed for each time point, with error bars indicating standard deviation.