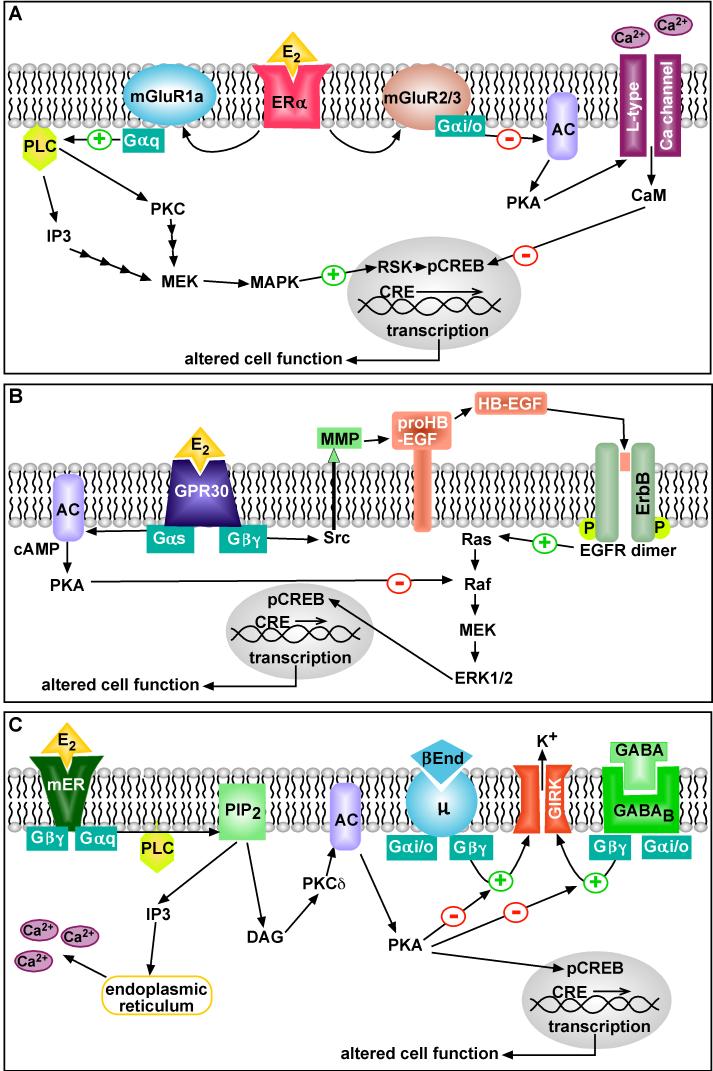
Figure 1. Cellular models of membrane-initiated signaling pathways of E2.
(A) E2 interacts with ERα locali zed at the neuronal (plasma) membrane and activates group 1 and group 2 metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1a, mGluR2/3) signaling. Activation of mGluR1a causes Gαq stimulation of phospholipase C (PLC) which leads to MAPK-induced CREB phosphorylation. Activation of mGluR2/3 causes Gαi/o inhibition of adenylyl cyclase (AC) and PKA which reduces the activity of L-type calcium channels and leads to attenuated CREB phosphorylation.
(B) E2 acts via GPR30 to promote EGF-receptor transactivation. This happens through a Gβγ-subunit pathway that promotes intracellular tyrosine kinase (Src)-mediated metalloproteinase (MMP)-dependent cleavage of proheparin-binding EGF (proHB-EGF) and release of HB-EGF from the cell surface. EGF redeptor transactivation leads to Ras-dependent ERK1/2 activation and presumably CREB phosphorylation. E2 via GPR30 can also stimulate adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity, which leads to PKA-mediated suppression of EGF-induced ERK1/2 activity.
(C) E2 activates a membrane-associated ER (mER) that is Gαq -coupled to activation of phospholipase C that catalyzes the hydrolysis of membrane-bound phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) to inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). Calcium is released from intracellular stores (endoplasmic reticulum) by IP3, and DAG activates protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ). Through phosphorylation, adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity is upregulated by PKCδ. The generation of cAMP activates PKA, which can rapidly uncouple GABAB and μ-opioid (μ) receptors from their effector system through phosphorylation of a downstream effector molecule (e.g., G protein-coupled, inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channel). The mER-mediated modulation of kinase pathways reduces the capacity of neuromodulators such as GABA and β-endorphin (β-End) to inhibit POMC neuronal excitability. mER-mediated activation of PKA can lead to phosphorylation of cAMP-responsive element binding protein (pCREB), which can then alter gene transcription through its interaction with CREs on genes.