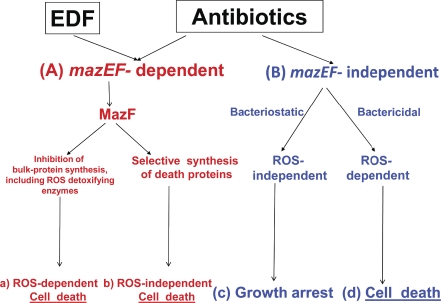
Figure 7. Alternative Death Pathways Induced by Some Antibiotics in.
E. coli
(A) Antibiotic induction of EDF-mazEF activates MazF (in red). (a) Antibiotics that inhibit transcription and/or translation cause cell death that is ROS-dependent, probably by inhibition of bulk-protein synthesis, including that of ROS detoxifying enzymes. (b) In contrast, antibiotics causing DNA damage trigger an ROS-independent death pathway(s), probably by the selective synthesis of death proteins.
(B) Antibiotic induction of EDF-mazEF-independent death pathways (in blue). (c) Antibiotics that inhibit transcription and/or translation do not cause ROS production. Therefore, they do not kill the cells but cause growth arrest, and thus are bacteriostatic. (d) In contrast, antibiotics that cause DNA damage do induce ROS production, and thereby lead to cell death.