Table 1.
Cytotoxicity, Antiviral and Anti-Integrase Activities of Derivatives 5–8
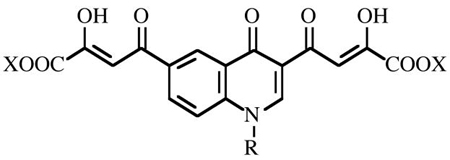 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-IN Activity
|
Antiviral Activity
|
|||||||||
| Cpd | R | X | IC50a |
CC50d | EC50e | SI f | ||||
| ST
|
3′-P
|
|||||||||
| Mg2+b | Mg2+c | Mn2+c | Mg2+c | Mn2+c | ||||||
| 5 | H | C2H5 | 77 ± 13 | 39 | 80 | 28 | >333 | >200 | >50 | - |
| 6 | H | H | 9.1 ±1.2 | 2.9 | 0.43 | 22 | >4.1 | >200 | 36.3 | 5.5 |
| 7 | Bzg | C2H5 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 21 | 40 | 191 | 20 | 9.6 |
| 8 | Bzg | H | 0.016 ± 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.012 | 0.44 | 0.20 | >200 | 4.29h | >47 |
| 2i | 1.83 | 7.8 | nrj | nr | - | |||||
| 3i | 6.5 | 82 | >25 | 61k | - | |||||
| 4i | 0.2 | 1.8 | 81 | 17 | 4.8 | |||||
Inhibitory concentration 50% (μM) determined from dose-response curves.
Experiments performed in triplicate using the BioVeris assay (ST assay in the presence of MgCl2).
Experiments performed on gels in the presence of MnCl2 or MgCl2 (see Figure 3).
Cytotoxic concentration 50% (μM).
Effective concentration 50% (μM).
Selectivity index = CC50/EC50.
Bz = CH2-4-F-Ph.
For this compound EC90 = 40 μM was determined.
nr: not reported.
Percentage of inhibition obtained at a concentration of 25 μM.
