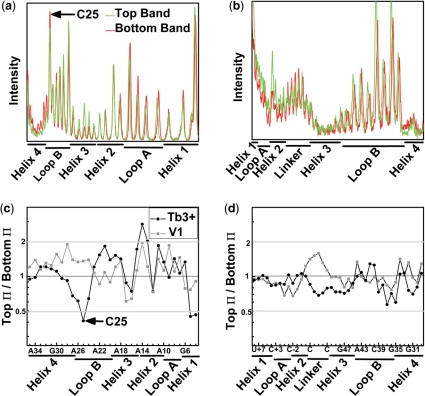
Figure 5.
Footprinting reveals identical secondary structures in the EMSA separated ribozyme species. Profiles of the Tb3+-mediated cleavage patterns of 32P-radiolabeled strand RzA (a) and strand RzB (b). The high degree of similarity between the T (top) and B (bottom) species indicates a shared secondary structure and suggests that the two species do not arise from gross misfolding of the ribozyme. Ratio of Π values, which represent averaged and normalized fractions of cleavage relative to background, are given for strands RzA (c) and RzB (d). Values <0.5 (gray line) indicate 2-fold greater sensitivity to Tb3+ (circles) or RNase V1 (squares) induced cleavage in the B species. Values >2 (gray line) indicate an at least 2-fold greater sensitivity in the T species.