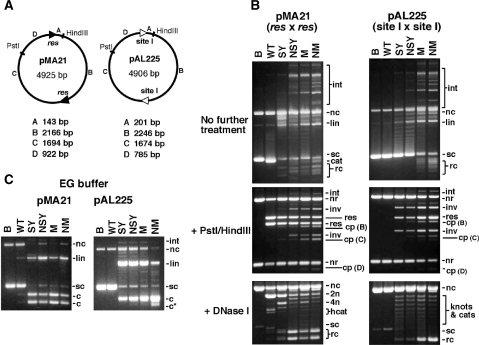
Figure 3.
In vitro recombination by wild-type resolvase and activated mutants. (A) Plasmid substrates pMA21 (res × res) and pAL225 (site I × site I). DNA segments between the recombination sites and restriction sites are denoted with letters A–D, and their sizes are given below each diagram. (B) Reactions of pMA21 and pAL225 with Tn3 resolvase and mutants. Following incubation with resolvase for 1 h, each sample was divided into three equal aliquots and separated by agarose gel electrophoresis without further treatment (upper panels), or digested with PstI and HindIII (centre panels), or nicked with DNase I (lower panels; 0.7% gel). DNase I-nicked intermolecular recombination products, with low gel mobility, are not shown. Lanes marked B are controls (incubated without resolvase). (C) Cleavage of pMA21 and pAL225 by Tn3 resolvase and mutants in EG buffer, which contains 40% ethylene glycol. The gels in parts B and C are annotated as follows: sc, supercoiled plasmid substrate; nc, nicked circular substrate; lin, linearized substrate plasmid; cat, supercoiled catenane resolution product; rc, free circular resolution product; int, intermolecular recombinant products; nr, non-recombinant restriction fragment; res, restriction fragment from resolution product; inv, restriction fragment from inversion product; cp, restriction fragment from cleavage product; 2n, 4n, 2-noded or 4-noded nicked catenane resolution product; hcat, 2-node catenane product nicked in only one DNA circle; c, product of cleavage at both recombination sites; c*, product of cleavage at a non-site I position.