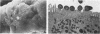Abstract
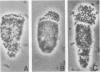
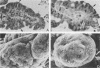
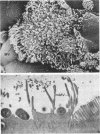
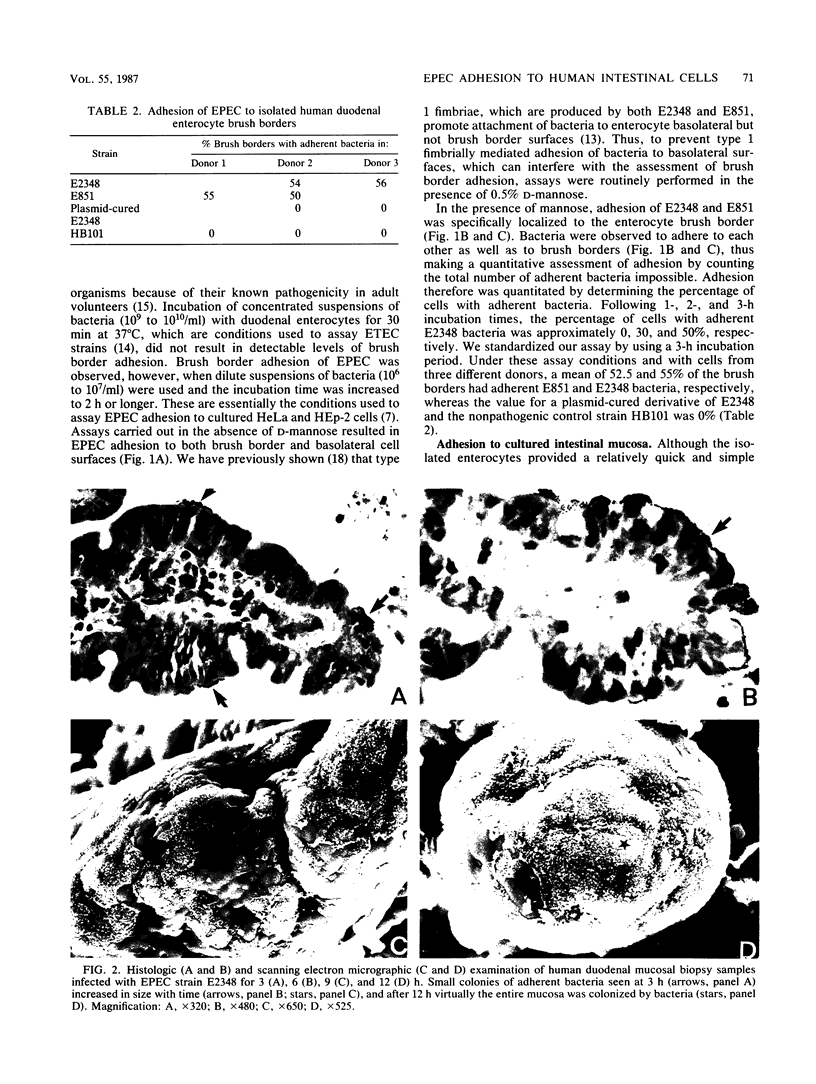
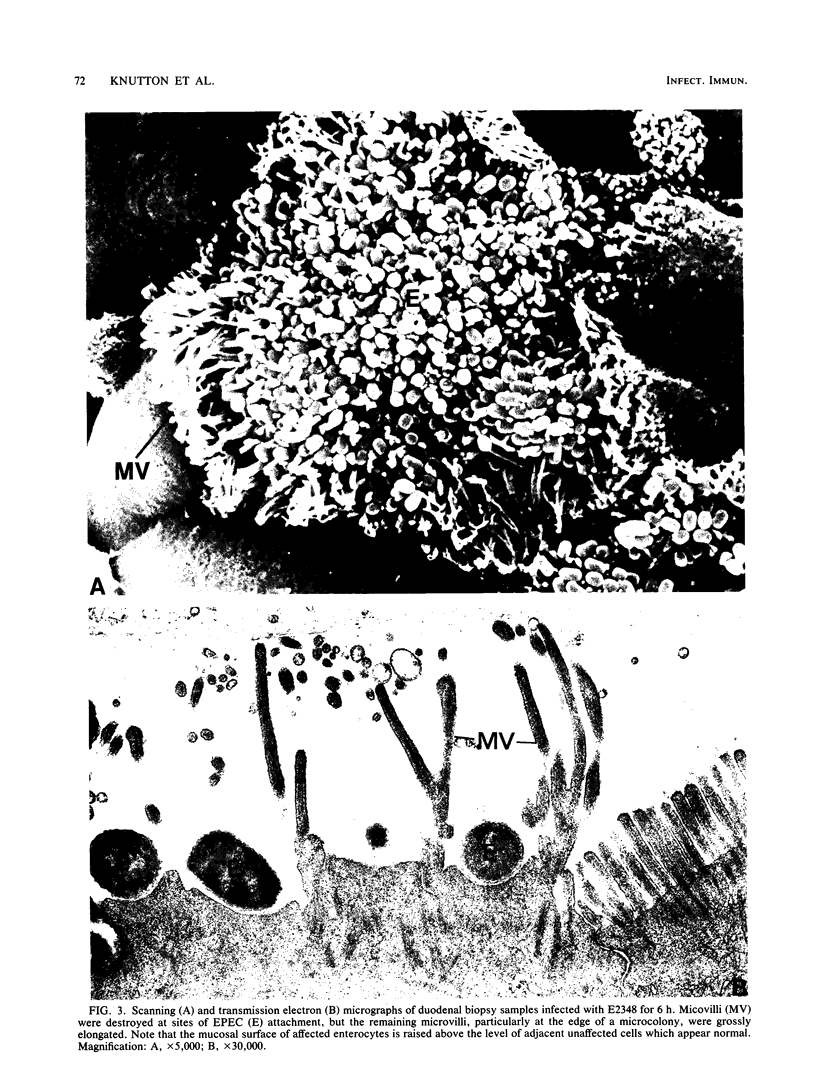
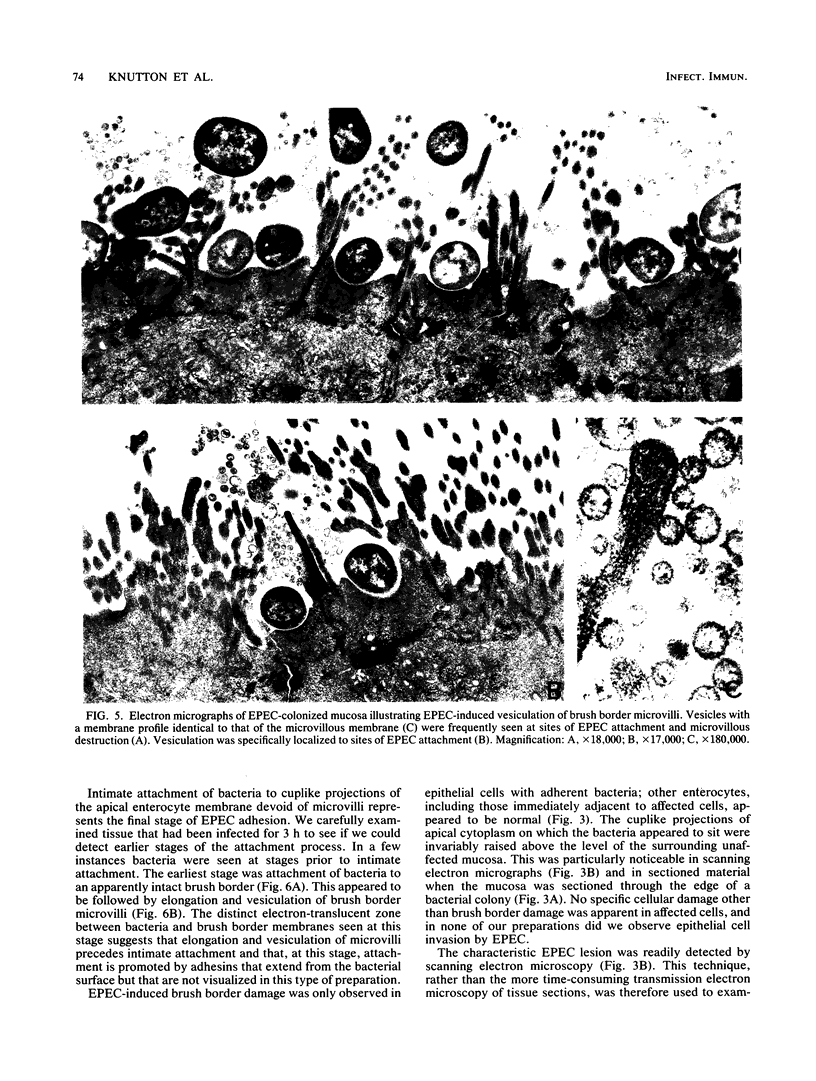
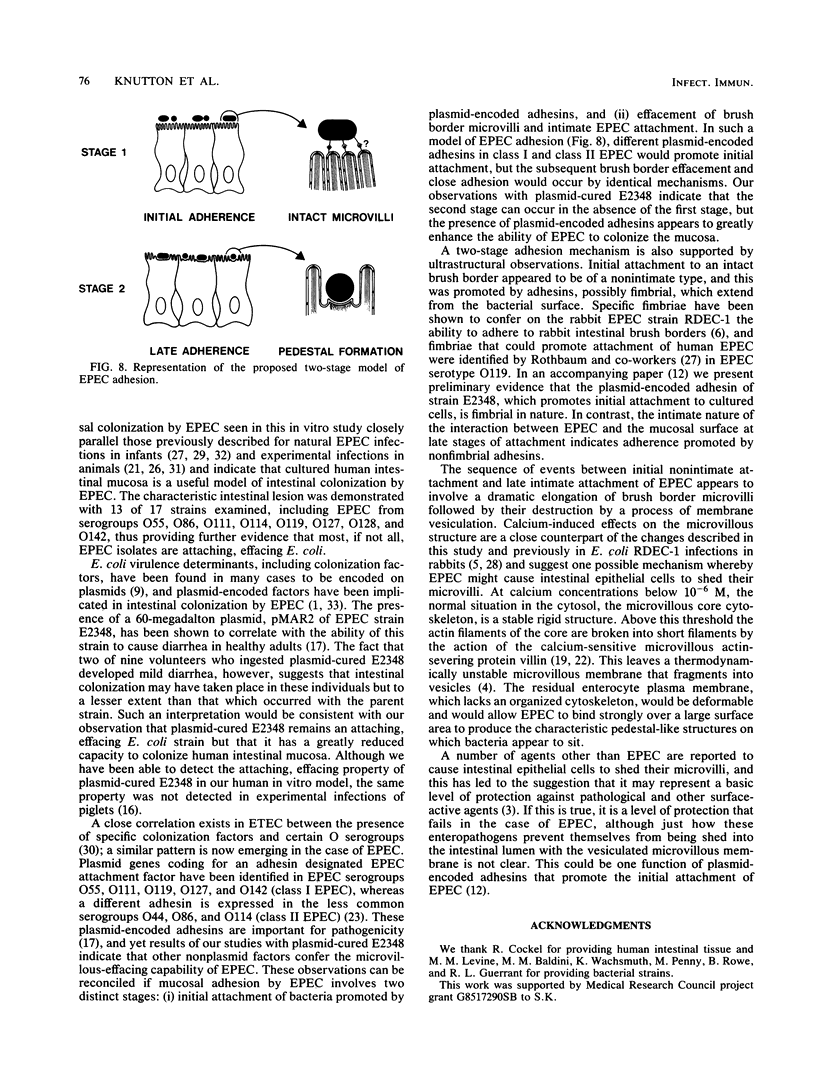
The adhesion of classic enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) strains of human origin to isolated human small intestinal enterocytes and cultured small intestinal mucosa was investigated. An adhesion assay with isolated human enterocytes prepared from duodenal biopsy samples was developed and tested with EPEC strains known to cause diarrhea in healthy adult volunteers. In the assay a mean of 53 and 55% of enterocytes had brush border-adherent E. coli E2348 (O127;H6) and E851 (O142:H6), respectively, whereas the value for a nonpathogenic control strain and a plasmid-cured derivative of strain E2348 was 0%. A collection of 17 EPEC strains was also tested for the ability to colonize cultured human duodenal mucosa. Extensive colonization occurred with 13 strains, including serogroups O55, O86, O111, O114, O119, O127, O128, and O142; and in each case electron microscopic examination of colonized mucosa revealed the characteristic histopathological lesion reported by others in natural and experimental EPEC infections. EPEC strains were seen to adhere intimately to the enterocyte surface, causing localized destruction of microvilli. The plasmid-cured derivative of strain E2348, which colonized cultured mucosa much less efficiently than the parent strain, nevertheless produced an identical lesion, indicating that plasmid-encoded factors are not essential for adhesion and the brush border-damaging property of EPEC.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning T. H., Trier J. S. Organ culture of mucosal biopsies of human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1423–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI106108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess D. R., Prum B. E. Reevaluation of brush border motility: calcium induces core filament solution and microvillar vesiculation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):97–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B., Inman L. R. Attachment of bacteria to intestinal epithelial cells in diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 in the rabbit: stages and role of capsule. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):219–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. P., Formal S. B., Schad P. A., Boedeker E. C. Genetic transfer of a mucosal adherence factor (R1) from an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain into a Shigella flexneri strain and the phenotypic suppression of this adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):711–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Levine M. M. From the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Summary of a workshop on enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1108–1118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Rowe B., Engert R. F., Short H. B., Gross R. J. Enterotoxigenicity of enteropathogenic serotypes of Escherichia coli isolated from infants with epidemic diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.171-178.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., McNeish A. S. Role of plasmid-encoded adherence factors in adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.78-85.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human small intestinal enterocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):824–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.824-831.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., Candy D. C., McNeish A. S. In vitro adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal epithelial cells from mucosal biopsies. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):514–518. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.514-518.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Rennels M. B., Daya V., Hughes T. P. Hemagglutination and colonization factors in enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):733–737. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Partial reconstruction of the microvillus core bundle: characterization of villin as a Ca++-dependent, actin-bundling/depolymerizing protein. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):648–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Turner P., Fleming J., Evans N. Mucosal adherence of human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):946–948. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A., Wharton K. A., Falco N., Howe C. L. Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):809–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E. Enteritis due to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli; present-day status and unsolved problems. J Pediatr. 1959 Aug;55(2):223–239. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(59)80091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polotsky Y. E., Dragunskaya E. M., Seliverstova V. G., Avdeeva T. A., Chakhutinskaya M. G., Kétyi I., Vertényl A., Ralovich B., Emödy L., Málovics I. Pathogenic effect of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli causing infantile diarrhoea. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1977;24(3):221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Inman L. R., O'Hanley P. D., Cantey J. R., Lushbaugh W. B. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of Escherichia coli O15 (RDEC-1) enteric infection in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):686–694. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.686-694.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. J., Hart A., Batt R. M., McDougall C., McLean L. Ultrastructural and biochemical changes in human jejunal mucosa associated with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (0111) infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1986 Jan;5(1):70–73. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198601000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. V., Rowe B. The occurrence of colonisation factors (CFA/I, CFA/II and E8775) in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from various countries in South East Asia. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;171(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02124915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. H., Sedgwick M. I., Evans N., Turner P. J., George R. H., McNeish A. S. Adherence of an enteropathogenic strain of Escherichia coli to human intestinal mucosa is mediated by a colicinogenic conjugative plasmid. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):393–402. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.393-402.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]