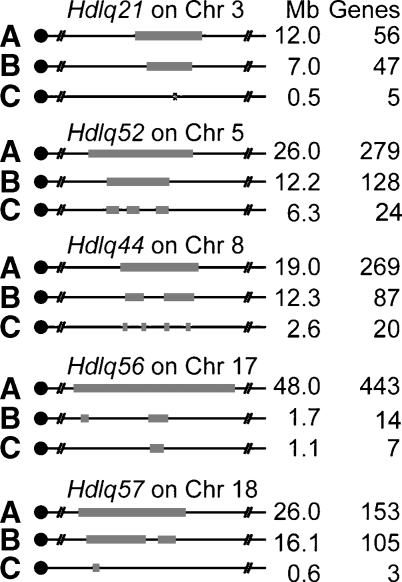
Fig. 6.
Narrowing QTL by bioinformatics. A: The 95% confidence interval (CI) and the number of gene in each QTL identified in cross B6 × 129; B: Comparative genomics. QTLs were narrowed by homology with human HDL QTL. Hdlq21 was homologous with human 1p31.3–21.3 (Mb 93–100); Hdlq52 was homologous with human 7q21–31.2 (Mb 81.1–84.6, Mb 86.3–92, Mb 102–105); Hdlq44 was homologous with human 8p23–22 (Mb 19–20), 22q11.2–q12.3 (Mb 32–34.3) and 4q28.3–q31.2 (Mb 141–150); Hdlq56 was homologous with human 6p12.3–q12 (Mb 49.5–49.9), 3p25 (Mb 52.9–53.2), and 2q13 (Mb 107.2–108.2); and Hdlq57 was homologous with human 18q12.1–22.2 (Mb 18–33, Mb 37–39) and 2q14.3–23.3 (Mb 127.5–128.4). C: Haplotype analysis. Each QTL was reduced by analyzing the haplotypes of the strains involved in the QTL crosses (Table 3) (15).