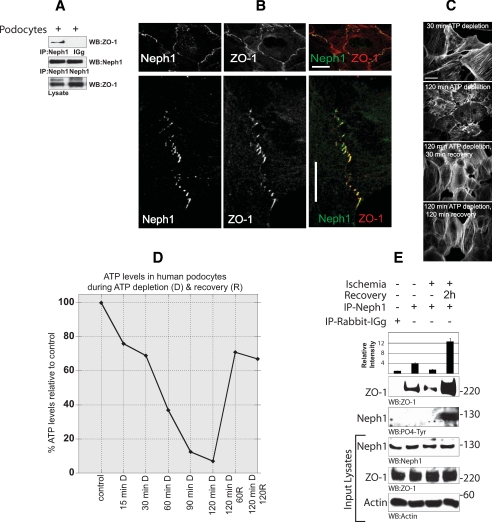
FIGURE 2.
Neph1 and ZO-1 are localized at the cell-cell junction in cultured podocytes. A, lysate obtained from the cultured human podocyte cell line was immunoprecipitated (IP) with Neph1 antibody and immunoblotted with Neph1 and ZO-1 antibodies. B, localization of Neph1 and ZO-1 in the podocyte cell line was examined by staining the cells with Neph1 and ZO-1 antibodies. Immunofluorescence analysis was done using confocal microscopy. Colocalization of Neph1 and ZO-1 at the membrane junctions appears yellow on merged images. Ischemia results in dissociation of Neph1 and ZO-1. C and D, podocyte cells were subjected to ATP depletion by antimycin A for the indicated times. Following ATP depletion, the medium was replaced with fresh growth medium, and the cells were grown for an additional 30 and 120 min. At each time point, the cells were stained with actin (C), and relative ATP levels were determined using the Promega Enliten ATP assay system (D). E, the cells were subjected to injury by treatment with ischemia for 120 min. Following injury, the medium in the cells was replaced with fresh growth medium, and the cells were grown for an additional 2 h. The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with Neph1 antibody. The presence of ZO-1 in the immune complex was examined by immunoblotting with ZO-1 antibody. Relative binding of ZO-1 with Neph1 during ischemia and recovery is also presented in the form of a bar diagram, where data are presented as a mean of three independent experiments.