FIGURE 5.
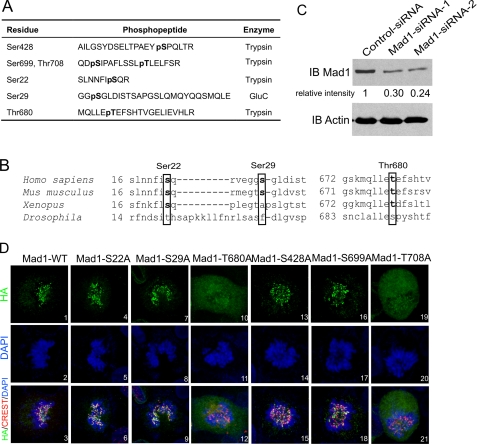
Identification of phosphorylated residues in Mad1 by LC-MS/MS spectrometry. A, phosphopeptides identified by MS/MS from FLAG-Mad1 immunoprecipitated (IP) from cells without or with Plk1 overexpression. Mad1 phosphorylation at Ser428, Ser699, and Thr708 was seen in mock transfected cells. Three additional phosphorylation sites, Ser22, Ser29, and Thr680 were identified in cells overexpressing transfected Plk1. The proteases used to generate the respective phosphopeptides are indicated. B, sequence alignment of Ser22, Ser29, Thr680 (in boxes) and their surrounding residues in Mad1 from H. sapiens, M. musculus, X. laevis, and D. melanogaster. C, depletion of cell endogenous Mad1 by siRNA. Two sets of Mad1 siRNA duplex were used (as described under “Experimental Procedures”). A ∼70% knockdown in the bulk cell culture was achieved 48 h after transfection. D, subcellular distributions of HA-tagged (green) Mad1-WT or S22A, S29A, T680A, S428A, S699A, and T708A mutants in cells knocked down for endogenous Mad1 using siRNA. CREST serum was used to stain centromeres (red). DNA is in blue. Sum of z-stack images is shown. IB, immunoblot.