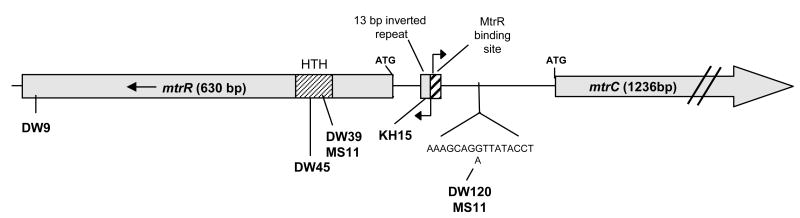
Figure 1. Location of mtr locus mutations used in this study.
A schematic of the N. gonorrhoeae mtr locus is shown. The α-helix-encoded region (HTH) of MtrR used for DNA binding is indicated by the hatched pattern. This region is the location of the mutations found in strains DW39, DW45, and MS11. The E202G mutation harbored in strain DW9 is located at the C-terminal end of the MtrR protein, which is hypothesized to be involved in the dimerization of MtrR to itself. The mtrR and mtrCDE transcriptional start sites are indicated by the arrows and are within the intergenic region that contains the MtR binding site and the 13 bp inverted repeat, which is the region where the mutation in strain KH15 is found (Hagman et al., 1995b). The mtr120 mutation occurs further upstream of the DNA binding region and is present in strains MS11 and DW120. This mutation has not been described previously, and the G to A change is shown in the detailed DNA sequence.