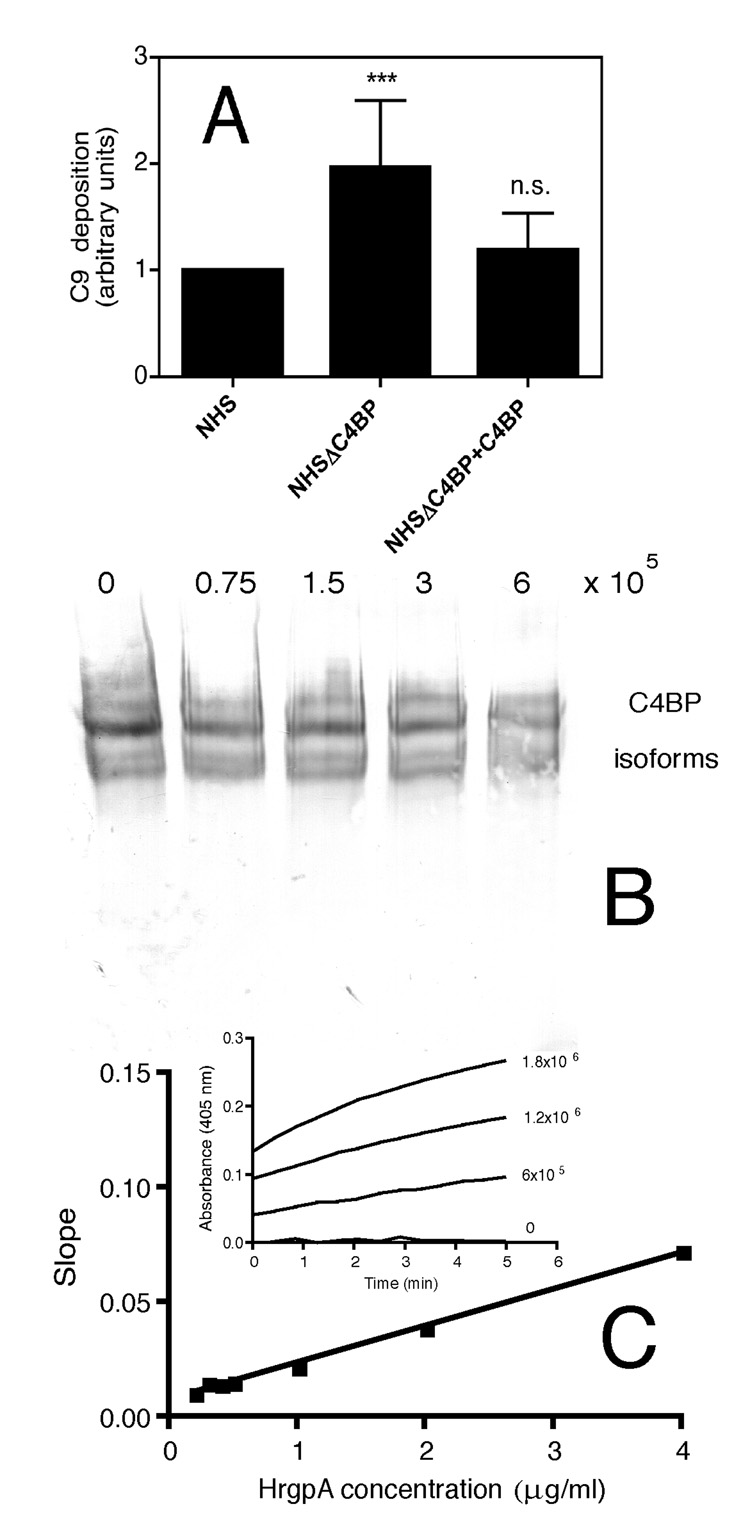
Fig. 6. In the absence of C4BP P. gingivalis is more readily attacked by complement.
A) P. gingivalis strain J4261 was harvested after 9 days of culture. 6 × 105 cells were incubated in a total volume of 50 µl with 5% NHS in GVB++, 5% NHS lacking C4BP and 5% C4BP-depleted NHS reconstituted with C4BP, respectively. Thereafter, deposition of C9 on bacteria was investigated using polyclonal antibodies followed by flow cytometry analysis. Heat inactivated serum (56°C, 30 minutes) was used as negative control and the background value was subtracted from the responses obtained in the sera experimentation. The values are presented relative to the signal obtained with NHS. Statistical significance of differences between depleted and reconstituted sera and NHS was estimated with Student’s t test, *** p<0.001, n.s. – not significant B) NHS incubated with indicated amounts of the J4261 strain under the same conditions as in A was analyzed by western blotting under non-reducing conditions and C4BP detected with monoclonal antibodies. Under these conditions several isoforms of C4BP are separated C) Indicated concentrations of purified HRgpA were incubated with 1mM L-BAPNA and the kinetic reaction was followed by measurement of absorbance at 405 nm corresponding to the released product. The slopes of obtained linear curves were plotted against concentration of HRgpA. The strain J4261 at indicated concentrations was then incubated with L-BAPNA (insert).