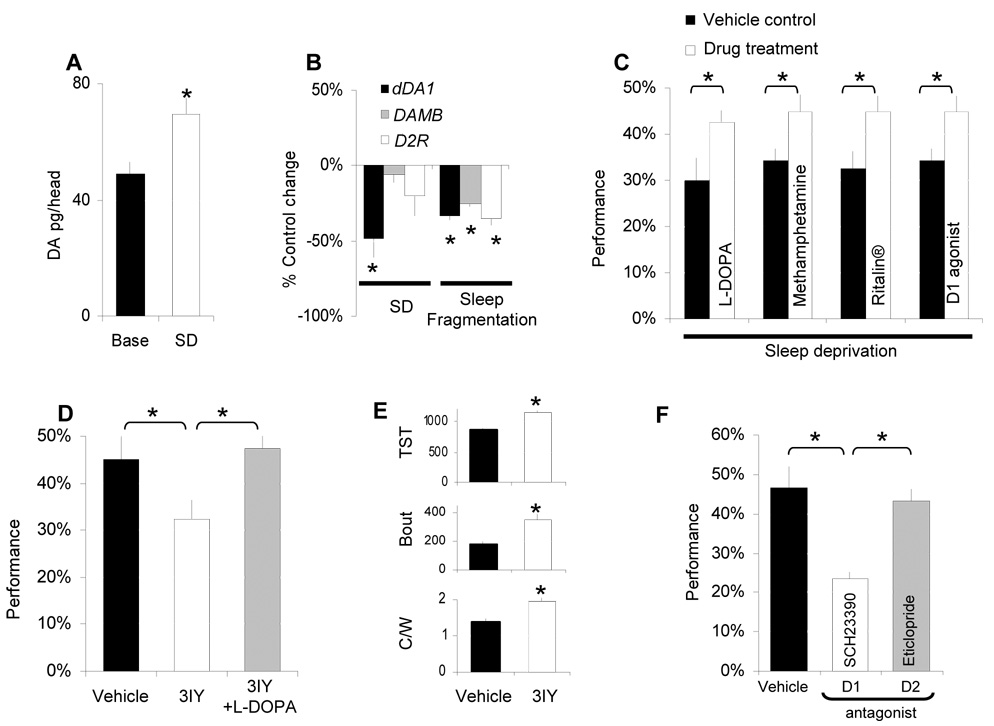
Figure 5. DA, extended waking and learning.
A, Whole head DA levels, measured by HPLC, are increased following 12 h SD compared to untreated circadian matched controls. B, dDA1 transcripts are down regulated by 12 h SD whereas mRNA levels for the other D1 like receptor DAMB and for the D2 receptor (D2R) remain stable. All three receptors are transcriptionally down regulated in the flies with spontaneous sleep fragmentation described in Figure 1F (data are presented as % change from controls, one-sample t-test). C, Performance impairments after 12hSD are reversed when flies are fed methamphetamine (1mg/mL), L-DOPA (5mg/mL), Ritalin (2.5mg/mL) or the D1 agonist SKF-82958 (3mg/mL). Learning was evaluated between ZT0-ZT3:59; D, Blocking DA synthesis by feeding flies 3IY (10mg/mL) for 36 h results in performance impairments. Co-administering flies 3IY and L-DOPA (10mg/mL) rescues learning. E, Total sleep time (TST in minutes), average sleep bout duration (Bout in minutes) and locomoter activity during waking (C/W) are significantly increased in flies on 3IY. F, Feeding flies the D1 receptor antagonist SCH-23390 (1mg/mL) but not the D2 antagonist eticlopride (1mg/mL) for 2 h (ZT0-ZT2) before the test impairs performance. (*:p<0.05).