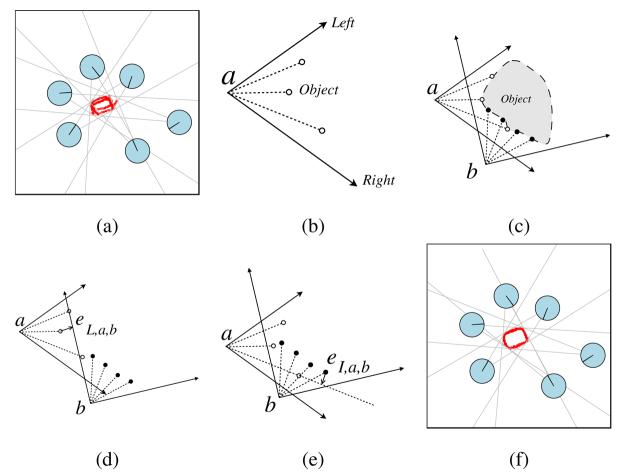
Fig. 4.
(a) The shape percept is a set of situated views of the physical object. A single situated view consists of the robot's pose, the tracker's support and the sensory observation. (b) The object is bounded by rays on the left and right. (c) The sensor readings from one situated view must fall within the bounding rays from all other situated views. (d) Exterior error vectors are defined from violations of this geometric constraint. A left error vector (eL,a,b) is shown here and a right error vector (eR,a,b) is defined similarly [18]. (e) An interior error vector (eI,a,b) is defined from sensor readings that come from the inside of an object. (f) A consistent shape description is created by minimizing the lengths of these error vectors.