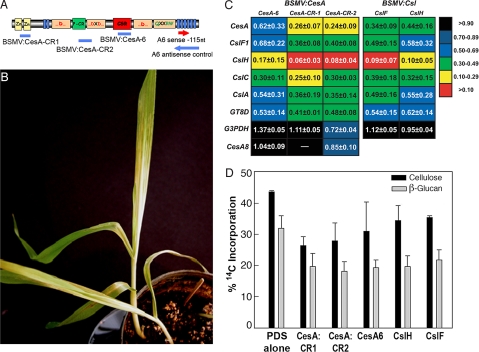
Fig. 3.
VIGS of the CesA gene superfamily in barley. (A) Schematic indicating the protein domains encoded by CesA mRNAs (28). Blue bands indicate the regions of the CesA cloned into the VIGS constructs used in these experiments. VIGS fragments were designed to silence the CesA gene family as well as the HvCesA6 gene. Red and blue arrows indicate the directional sequence used for sense and antisense riboprobe synthesis, respectively. (B) Onset of silencing is detected by photobleaching as a result of the cosilencing of phytoene desaturase. (C) Silencing of CesAs, CslHs, and CslFs by VIGS results in a global reduction in the expression of genes involved in cell wall biosynthesis. Expressions of CesA6, Csl, GT-8D, and G3PDH genes in plants infected with respective VIGS constructs, assayed by comparative qRT-PCR, are the mean ± SD of 3–5 biological replicates, are relative to plants infected with empty vector-PDS control plants, and are normalized to ubiquitin10 gene expression. (D) Incorporation of D-14C-Glc into cellulose and β-glucan are a percentage of the total radioactivity of each cell wall polymer ± SD of 3 biological replicates.