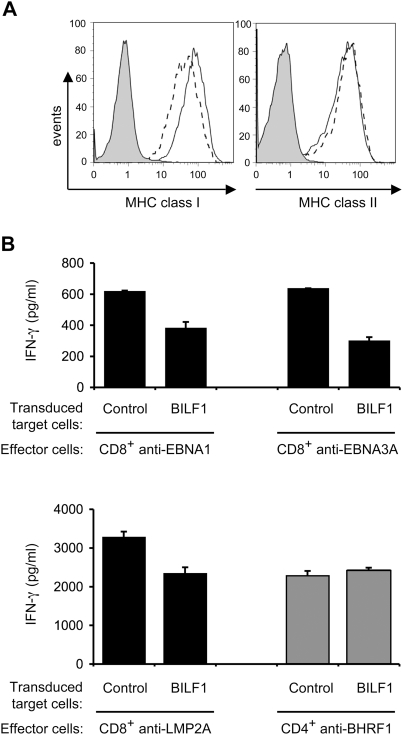
Figure 4. BILF1 downregulates surface MHC class I expression and inhibits the T cell recognition of endogenous EBV antigen in LCLs.
(A) LCLs were transduced with PLZRS-HABILF1-IRES-GFP retrovirus. After 6 days, surface MHC class I was stained with PE-conjugated W6/32 mAb and MHC class II was stained with PE-conjugated anti-DR mAb, YE2/36-HLK. Two-colour flow cytometry was used to analyze staining in the untransduced, GFP−, population, shown as the solid line histogram, and in the transduced GFP+ (BILF1+) population, shown as the dashed line histogram. The grey histogram denotes background staining obtained with an isotype control PE-conjugated antibody. (B) LCL cultures transduced with control retrovirus or with the BILF1 retrovirus were sorted by flow cytometry to generate GFP+/BILF1− and GFP+/BILF1+ lines to use as targets in assays with EBV-specific T cells. The control and BILF1+ LCL targets were incubated with HLA-matched CD8+ effector T cells clones specific for EBNA1 (HPV), EBNA3A (YPL), or LMP2A (CLG) peptides, or a CD4+ effector T cell clone specific for a BHRF1 (PYY) peptide. After 18 hrs the supernatants were tested for the release of IFN-γ as a measure of T cell recognition. All results are expressed as IFN-γ release in pg/ml and error bars indicate standard deviation of triplicate cultures.