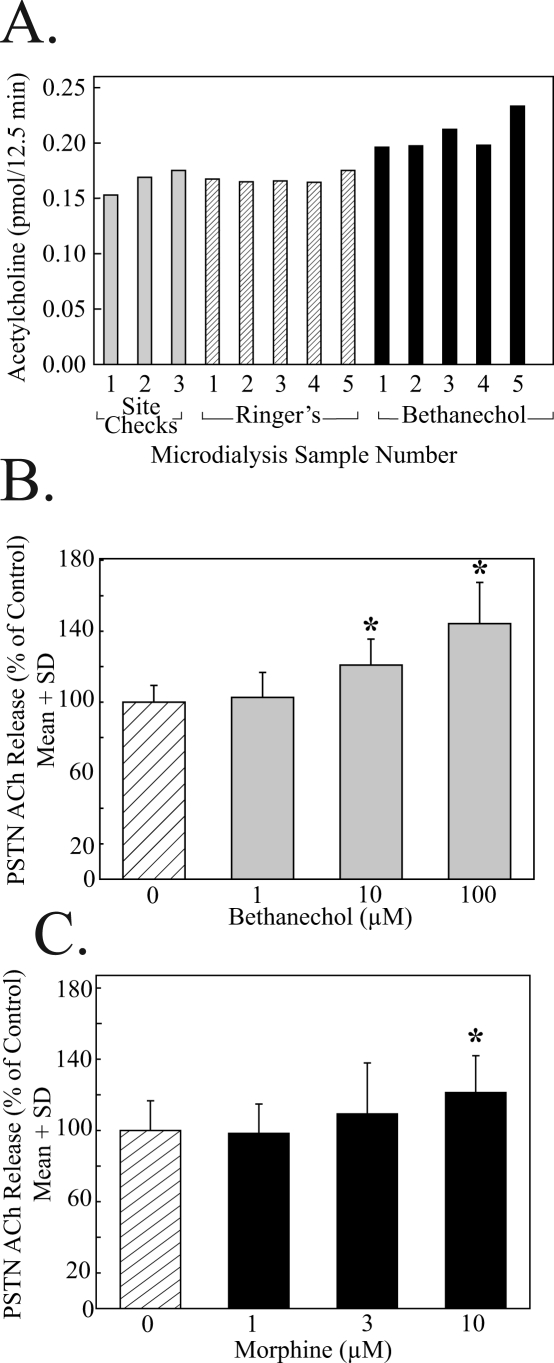
Figure 2.
Acetylcholine (ACh) release in the principal sensory trigeminal nucleus (PSTN) was increased during dialysis delivery of bethanechol or morphine. A. Time course of a single, representative, microdialysis experiment quantifying ACh release in PSTN during dialysis with Ringer's solution (control) followed by dialysis delivery of the muscarinic cholinergic agonist bethanechol. One rat was used for each experiment, and, for a given experiment, the 5 ACh values associated with the Ringer's solution condition were averaged together to provide mean control ACh levels. Similarly, the 5 ACh values measured during dialysis drug delivery were averaged together to obtain mean druginduced ACh levels. Multiple animals were tested for each drug concentration. These data were averaged together, and inferential statistics were used to evaluate the hypothesis that ACh release varied as a function of drug concentration. B. Group data showing that bethanechol caused a significant (*) concentration-dependent increase in PSTN ACh release. Each concentration of bethanechol was delivered to the PSTN of 3 rats. C. Dialysis delivery of morphine to the PSTN significantly (*) increased ACh release. Each concentration of morphine was tested using 3 animals.