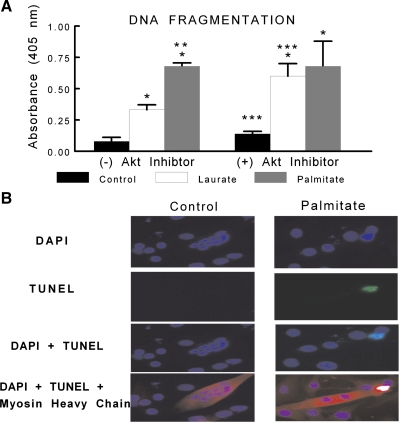
Fig. 5.
C2C12 myotubes were treated under control, palmitate, or laurate conditions as described in Fig. 1. The DNA fragmentation ELISA measures cytosolic mono- and oligonucleosomes and was used as an indicator of apoptotic cell death. A: palmitate treatment significantly increased the content of cytosolic fragmented DNA. In addition, there was a combined effect of the FFA treatment and Akt inhibition, as treatment with laurate and 10 μM Akt inhibitor induced DNA fragmentation similar to that observed in the palmitate-treated myotubes. The data are expressed as OD × area (in arbitrary units) and are displayed as means ± SE. *Experimental vs. control treatment (P < 0.05); **palmitate vs. laurate groups (P < 0.05); ***(+) Akt inhibitor vs. (−) Akt inhibitor (P < 0.05). B: representative terminal deoxynucleotidyl-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining (green) of control- and palmitate-treated myotubes, as described in Fig. 1, colabeled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue) and myosin heavy chain (red).