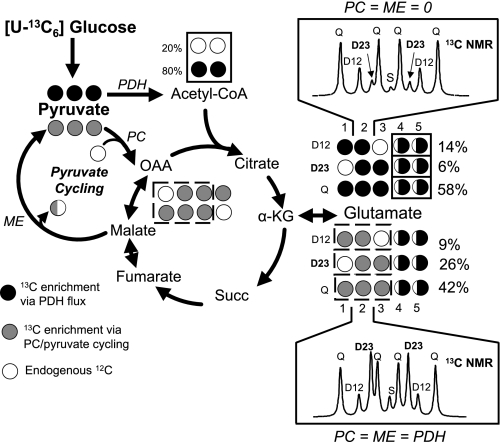
Fig. 2.
Schematic summary of 13C-NMR technique for measurement of pyruvate cycling. The technique involves incubation of β-cell lines with [U-13C6]glucose, extraction of glutamate and analysis of 13C isotopomers by 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Shown for example are spectra of carbon-2 of glutamate simulated using tcaSim (8, 28, 37) under two idealized situations. Top: the spectrum obtained if pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is the sole pathway for pyruvate to enrich α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and glutamate (20% unlabeled endogenous substrate is also assumed). Bottom: the spectrum obtained when PDH and pyruvate carboxylase (PC) flux contribute equally to pyruvate entry into the TCA cycle. Several changes in the glutamate isotopomer populations occur as result of PC activity. For example, notice that carboxylation of pyruvate by PC leads to the loss of enrichment in the C1 position and a dramatic increase in the isotopomer population detected as a D23 multiplet. In experimental data, the isotopomer populations determined by the 13C-NMR multiplets of all glutamate carbons are used to calculate relative flux through the oxidative (PDH) and anaplerotic (PC) entry points into the TCA cycle. It is assumed that pyruvate cycling is equivalent to PC flux. See text and refs. 8, 28, and 37 for more details.