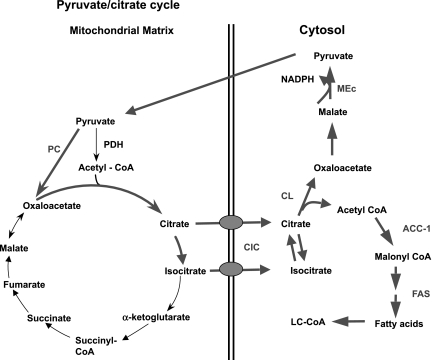
Fig. 4.
Pyruvate/citrate cycle. In this cycle, pyruvate also enters the TCA cycle via PC. The oxaloacetate formed in the PC reaction then condenses with acetyl-CoA to form citrate and isocitrate, which can exit the mitochondria via the citrate/isocitrate carrier (CIC). Once in the cytosol, citrate is cleaved to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA by ATP-citrate lyase (CL), with these two products being metabolized further by two separate pathways. Oxaloacetate is recycled to pyruvate via conversion to malate and engagement with the MEm or MEc to reform pyruvate. Acetyl-CoA goes on to form malonyl-CoA in the acetyl-CoA carboxylase-1 (ACC1) reaction and can then be used for synthesis of long-chain acyl-CoAs (LC-CoA) via fatty acid synthase (FAS).