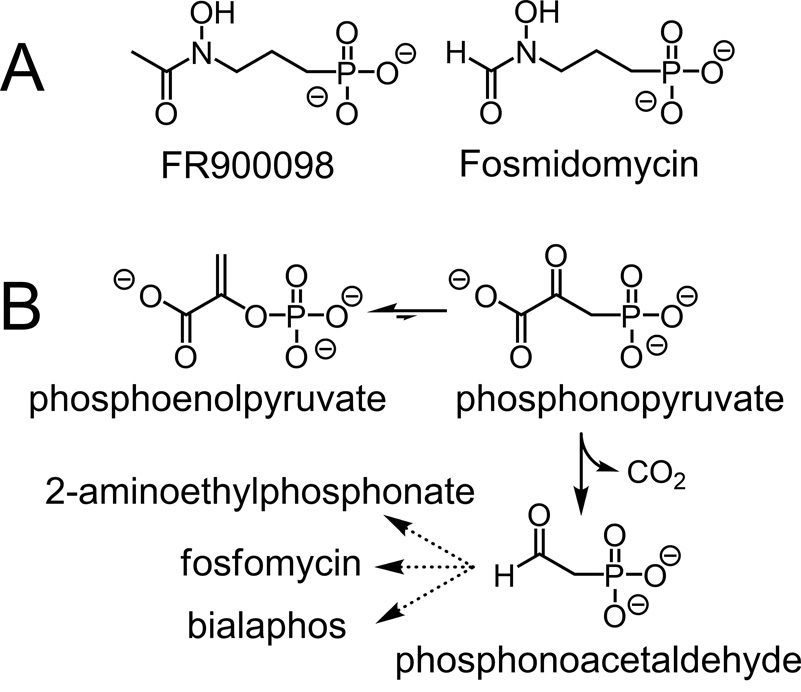
Figure 1.
(A) The structures of the antimalarial compounds FR900098 and fosmidomycin. Both inhibit DXR, an essential enzyme in the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in malaria-causing parasites. (B) The initial reactions in the biosynthesis of 2-aminoethylphosphonic acid, fosfomycin, and bialaphos. In the first step, catalyzed by PEP mutase, phosphoenolpyruvate is rearranged to phosphonopyruvate, which is then decarboxylated to yield phosphonoacetaldehyde in a reaction catalyzed by phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase.