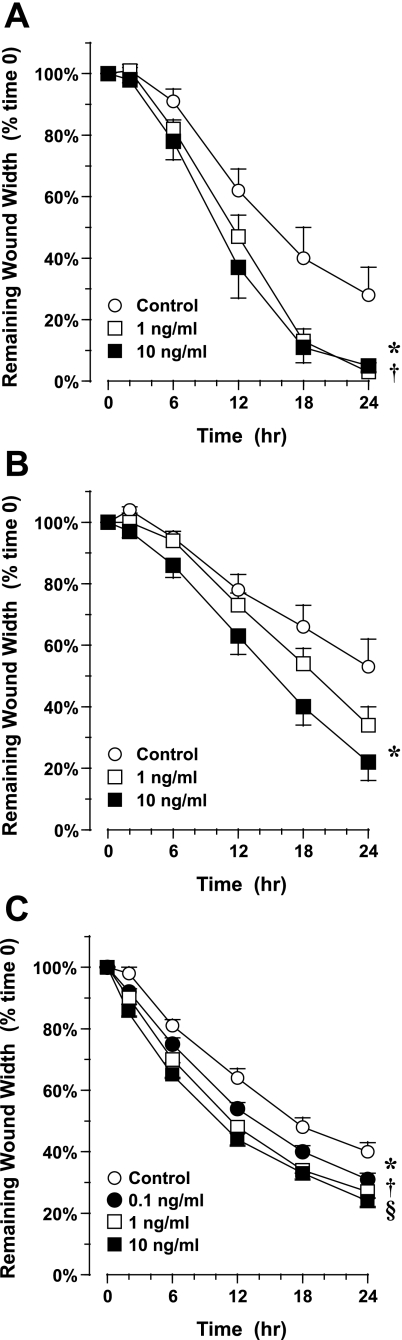
Fig. 2.
Migration of airway epithelial cells (AEC) in response to IL-1β. Cells were injured using a rubber stylet, and migration was followed for 24 h by digital photomicroscopy. A: migration of primary AEC grown under ALI culture conditions for 1 wk. Treatment with 1 or 10 ng/ml IL-1β at the time of injury accelerated migration. Values are means ± SE (n = 8–10 experiments in cells collected from 3 normal donors). *P = 0.02; † P = 0.01 vs. control. B: migration of primary AEC grown under ALI culture conditions for 3 wk. Cells were injured and treated with 1 or 10 ng/ml IL-1β as described in A. Treatment with 10 ng/ml IL-1β at the time of injury accelerated migration. Values are means ± SE (n = 10 experiments in cells collected from 3 normal donors). *P = 0.01 vs. control. C: migration of 16HBE14o− cells in response to IL-1β. Confluent monolayers in submersion culture were injured with a rubber stylet. Treatment with 0.1–10 ng/ml IL-1β at the time of injury accelerated migration. Values are means ± SE (n = 8 experiments). *P = 0.01; †P = 0.0003; §P = 0.0001 vs. control.