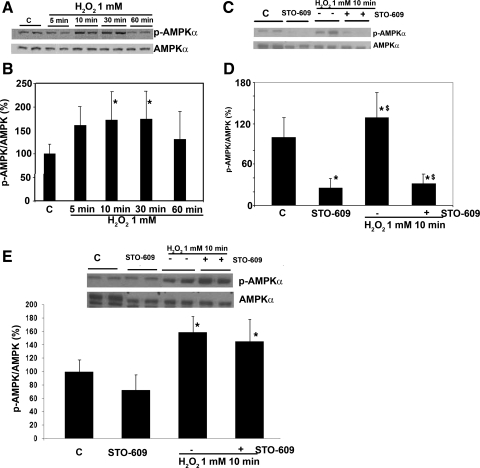
Fig. 2.
Effect of H2O2 on AMPK phosphorylation in HeLa cells. A and B: similar to the findings with H4IIEC3 cells, the levels of AMPK phosphorylation in HeLa cells were increased after H2O2 (1 mM) treatment to 1.2-fold over control at 10 min after treatment with 1 mM H2O2 (P < 0.05). C and D: AMPK phosphorylation in HeLa cells was affected by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase (CaMKK) inhibitor, STO-609 at a concentration of 1 μg/ml. At baseline, STO-609 significantly inhibits AMPK phosphorylation by 75%, and it also significantly prevents AMPK activation in response to H2O2. To further examine the major pathway for the activation of AMPK by H2O2, similar experiments were performed in H4IIEC3 cells in the presence of STO-609 (E). Contrary to the experiments in the HeLa cells, STO-609 did not significantly inhibit AMPK phosphorylation at baseline. The activation of AMPK by H2O2 persists despite the presence of STO-609. Means ± SE (the blot is a representative of 3 blots from 3 individual experiments) are shown. *Significant difference vs. control; P < 0.05, by one-way ANOVA; $significant difference compared with cells that were not treated with STO-609.