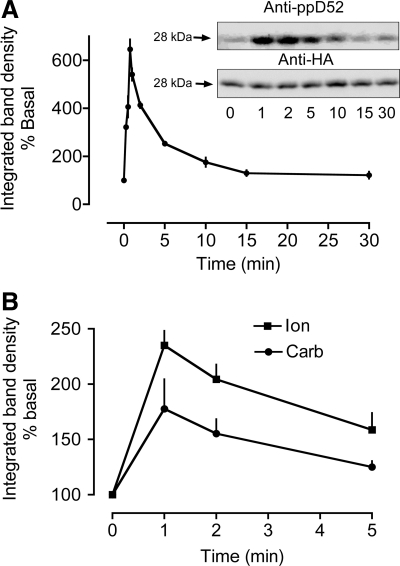
Fig. 5.
Time courses for calcium-dependent D52 S136 phosphorylation in HEK 293 cells and mouse gastric glands. S136 phosphorylation was quantified by using affinity-purified pS136 antibody that was produced by injecting rabbits with 2 phosphopeptides: Ac-CNSPTFK(pS)FEEKVEN-amide and Ac-NSPTF K(pS) FEEKVENC-amide. The antibody was affinity purified by passing immunized rabbit serum through an affinity column coupled to a nonphosphopeptide (Ac-CNSPTFKSFEEKVEN-amide) and then passing flowthrough fractions from this column through a second affinity column coupled to the 2 phosphopeptides. Phosphospecific antibodies were eluted from the latter column with low pH glycine. A: time course for carbachol stimulation of HEK293 cells (100 μM Carb, N = 3–8) expressing HA-D52. Cells were transfected with Effectene as described in Fig. 4. Inset: a representative experiment depicting Western blots of samples from HEK293 cells probed for S136 phosphorylation (anti-ppD52) and for the HA tag. The HA signals were used to correct for differences in HA-D52 expression levels. After normalization, S136 phosphorylation was expressed as % of basal. B: time courses for carbachol and ionomycin stimulation of mouse gastric glands. N = 3, 30 mice. 100 μM Carb, 3 μM Ion.