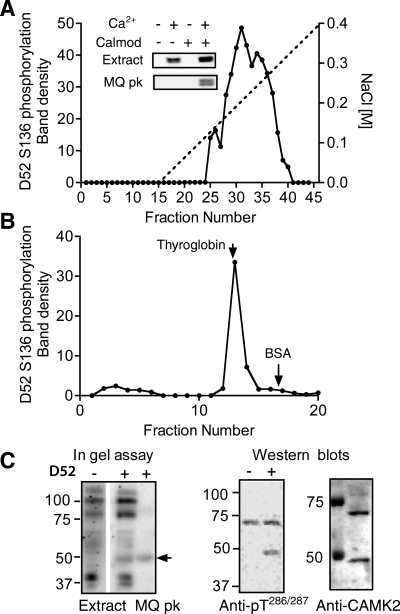
Fig. 7.
Characterization of D52 kinase in HEK293 cells. A: D52 kinase activity profile obtained after fractionation of HEK293 cell extract (100,000 g supernatant) on a Mono Q anion exchange column. Kinase activity in column fractions was analyzed by incubation of aliquots with recombinant His-tagged D52 protein in the presence of calcium/calmodulin/ATP followed by Western blotting with affinity-purified pS136 antibody. Inset: S136 phosphorylation assayed +/− calcium/calmodulin (Calmod) in the supernatant and in Mono Q peak fractions (nos. 30–36). B: D52 kinase activity profile of Mono Q peak after fractionation on a Superose 6 HR 10/30 size exclusion column. Arrows indicate elution positions of 2 external standards: thyroglobin (Mr 660,000) and BSA (Mr 68,000). C: migration patterns of the monomeric form of D52 kinase on SDS-PAGE gels. Left: “in gel” assay comparing phosphorylation patterns of the unfractionated extract and Mono Q peak in the absence (−) and presence (+) of His-tagged D52 protein in the gel. Arrow indicates the position of D52 phosphorylating activity that was detected when D52 included in the 10% SDS PAGE gel. Center: Western blot of Mono Q peak assayed +/− calcium/calmodulin (Calmod) and probed with anti-active CAMK2 antibody (anti-pT286/287). Samples were resolved on 8% SDS PAGE gels prior to Western blotting. Right: Western blot of the same Mono Q peak probed with anti-CAMK2 antibody (Stressgen). The identity of the ∼70-kDa protein detected on this blot and the anti-pT286/287 blot is unknown.