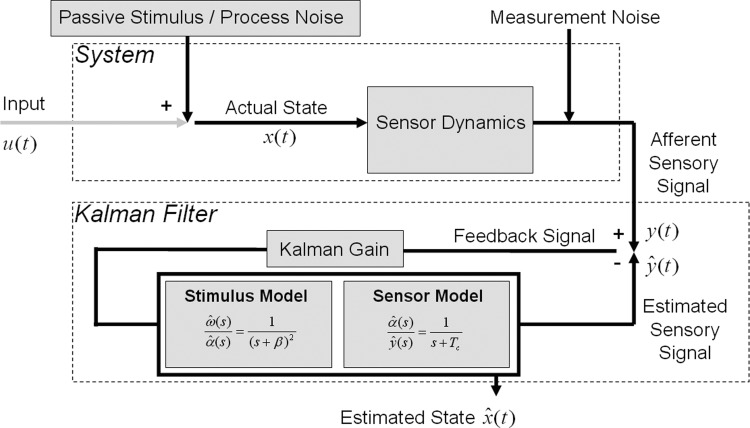
FIG. 4.
Kalman filter model (after Borah et al. 1988). A simplified version is depicted to illustrate how the Kalman filter approach parallels the Observer model in Fig. 3. The model resembles a passive observer, so input is set to 0, and motor dynamics (not shown) are set to unity transfer. The feedback signal is multiplied by the statistically optimal Kalman gain. The result is passed through the internal model of the system dynamics, which includes the stimulus internal model and the internal model of sensor dynamics. Note that the Kalman filter uses the state space representation of these internal models.