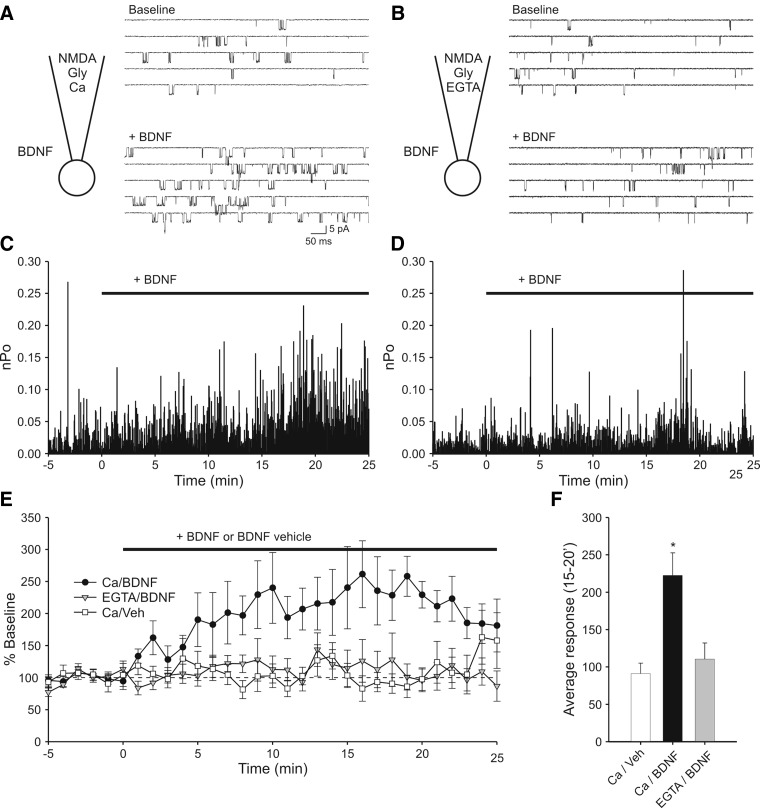
FIG. 5.
Cell-attached single-channel recording shows that local calcium entry is sufficient for BDNF modulation of NMDA receptor activity. A: diagram illustrating the recording conditions and sample sweeps indicating modulation of NMDA receptor activity by BDNF. In addition to NMDA, glycine and other ingredients (see methods), the pipette solution contained 1.3 mM calcium. The patch contained ≥2 channels. Top: recording of baseline activity. Bottom: increased activity elicited by bath perfusion of 20 ng/ml BDNF. B: sample activity from a recording in which calcium in the pipette solution was replaced by EGTA. The patch contained ≥2 channels. Top and bottom traces: baseline activity and activity in the presence of BDNF, respectively. In this case, perfusion of BDNF had no effect on NMDA receptor activity. C: plot of open probability (Po) vs. time during for the recording illustrated in A. Time = 0 has been set to onset of the BDNF perfusion. Baseline activity is defined as the 5 min prior to BDNF perfusion. Note that Po increases with time during the BDNF perfusion. D: Po plot for the recording illustrated in B. Note that replacing Ca with EGTA in the pipette solution resulted in no effect of BDNF on NMDAR activity. E: plot in which Po values have been combined into 1-min bins and normalized to baseline activity. Experiments in which calcium was present in the pipette solution and which were exposed to BDNF show elevated activity (○, n = 10). Experiments in which the pipette contained calcium but were exposed to BDNF vehicle solution did not (□, n = 10). Experiments in which patches were exposed to BDNF but contained EGTA instead of calcium in the pipette solution also showed no increase in activity (▾, n = 9). F: summary graph in which average activity at 15–20 min during the BDNF perfusion is plotted. Addition of BDNF elicited a significant increase in activity as compared with vehicle when calcium was in the pipette solution (*, P < 0.01) but not when EGTA was in the pipette solution (P > 0.4).