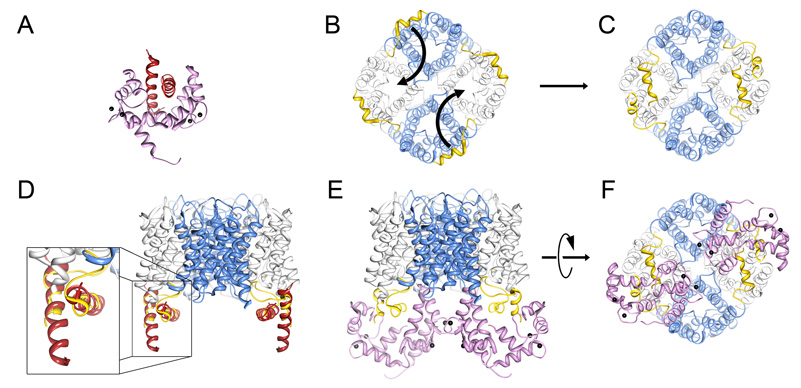
Figure 5. Model of the AQP0/calmodulin complex.
A, Structure of the petunia glutamate decarboxylase (PGD) calmodulin complex (Protein Data Bank Accession number 1NWD). Calmodulin wraps itself around two PGD α-helices oriented in an anti-parallel fashion. Ca2+ indicated by black speheres. B, AQP0 tetramer viewed from the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane (bottom view). The carboxyl terminal tails are highlighted in yellow. Curved arrows indicate the proposed movement of the carboxyl tails. C, Rotation of the AQP0 carboxyl terminal tails places neighboring AQP0CBD in close proximity in an orientation similar to the PGD calmodulin structure (Yap et al., 2003). D, Overlay of the PGD α-helices with AQP0CBD. E and F, Side and bottom views of the modeled AQP0/CaM complex, respectively. In this model, calmodulin obstructs only two of the water pores out of the AQP0 tetramer (grey versus blue). Structure fitting and modeling was performed in UCSF chimera (Pettersen et al., 2004).