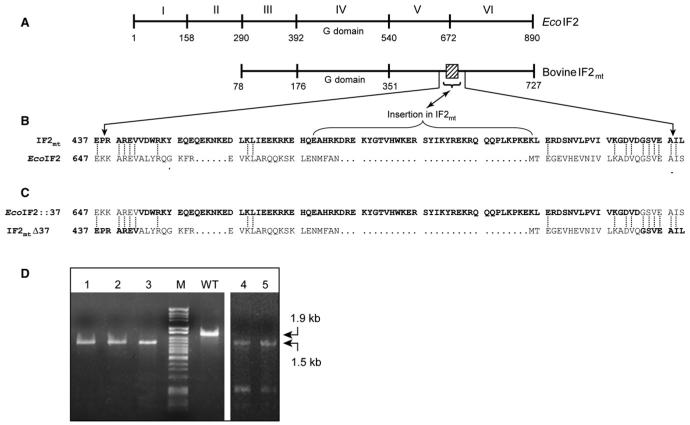
Figure 5. Chimeras of EcoIF2 and IF2mt.
(A) Schematic representation of the domain organization of EcoIF2 and bovine IF2mt. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions. IF2mt lacks the counterparts of EcoIF2 domains I and II. The 37 amino acid insertion conserved in mitochondrial IF2s is indicated by a box.
(B) Alignment of a portion of the sequences of EcoIF2 and bovine IF2mt (shown in bold letters). The identical residues are joined by a dotted line. The 37 amino acid insertion is marked by a bracket and is flanked by regions of high conservation, which were chosen for a swap between the two IF2s.
(C) The sequences of the resulting chimeras are shown.
(D) PCR analysis of ΔinfB::KanR transductants harboring either pACDH-IF2mtΔ37 (lanes 1-3) or pACDH-EcoIF2::37 (lanes 4 and 5) using IF2-FP5, IF2-RP3, IF2-KO-FP, and IF2-KO-RP (Figure 2A) to confirm replacement of infB with KanR. WT stands for wild-type, and M is DNA size marker (λ HindII + HindIII).