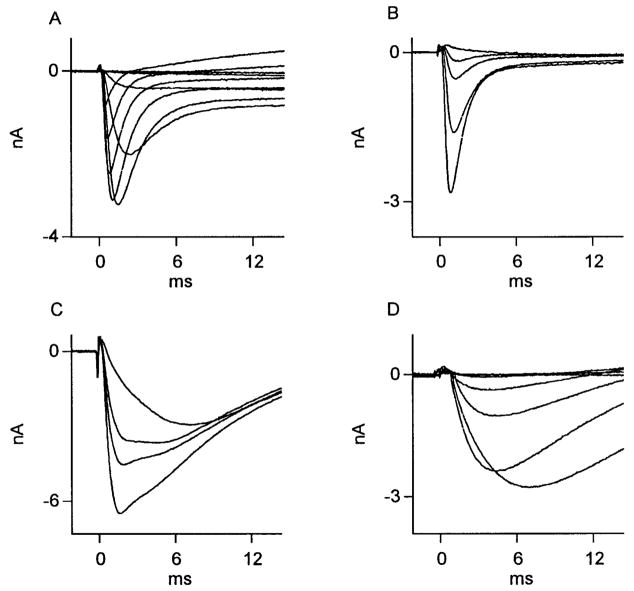
FIG. 8.
Effect of NGF treatment on Na+ currents in axotomized cutaneous neurons. Na+ currents recorded from 3 DRG neurons whose transected axons were perfused with NGF. Of 19 neurons studied, 6 expressed kinetically fast Na+ currents (A). Here, superimposed traces were recorded during test potentials from −50 to +30 mV in steps of 10 mV, after a fixed holding potential of −55 mV. Successive traces from same neuron during 1 μM TTX perfusion (B) revealed these currents to be entirely TTX sensitive. C and D: 13 of 19 neurons revealed presence of a kinetically slow TTX-resistant current. In C, successive Na+ current recordings at 0 mV from a conditioning potential of −60 mV during perfusion with TTX eliminate early, but not late portion of current. Fast, early component of Na+ current appeared to be lacking in 3 of 19 NGF-treated neurons, as depicted in D, which shows Na + current traces recorded from another neuron during test potentials from −50 to 0 mV in steps of 10 mV after a fixed holding potential of −60 mV (peak inward current was recorded at −10 mV). This neuron was not exposed to TTX.