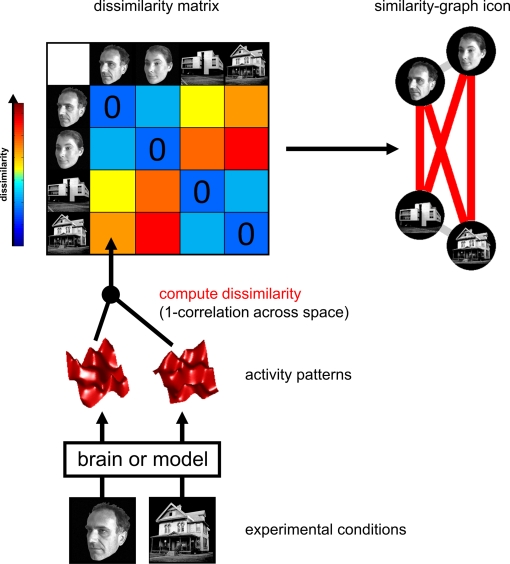
Figure 2.
Computation of the representational dissimilarity matrix. For each pair of experimental conditions, the associated activity patterns (in a brain region or model) are compared by spatial correlation. The dissimilarity between them is measured as 1 minus the correlation (0 for perfect correlation, 1 for no correlation, 2 for perfect anticorrelation). These dissimilarities for all pairs of conditions are assembled in the RDM. Each cell of the RDM, thus, compares the response patterns elicited by two images. As a consequence, an RDM is symmetric about a diagonal of zeros. To visualize the representation for a small number of conditions, we suggest the similarity-graph icon (top right, cf. Figure 1).