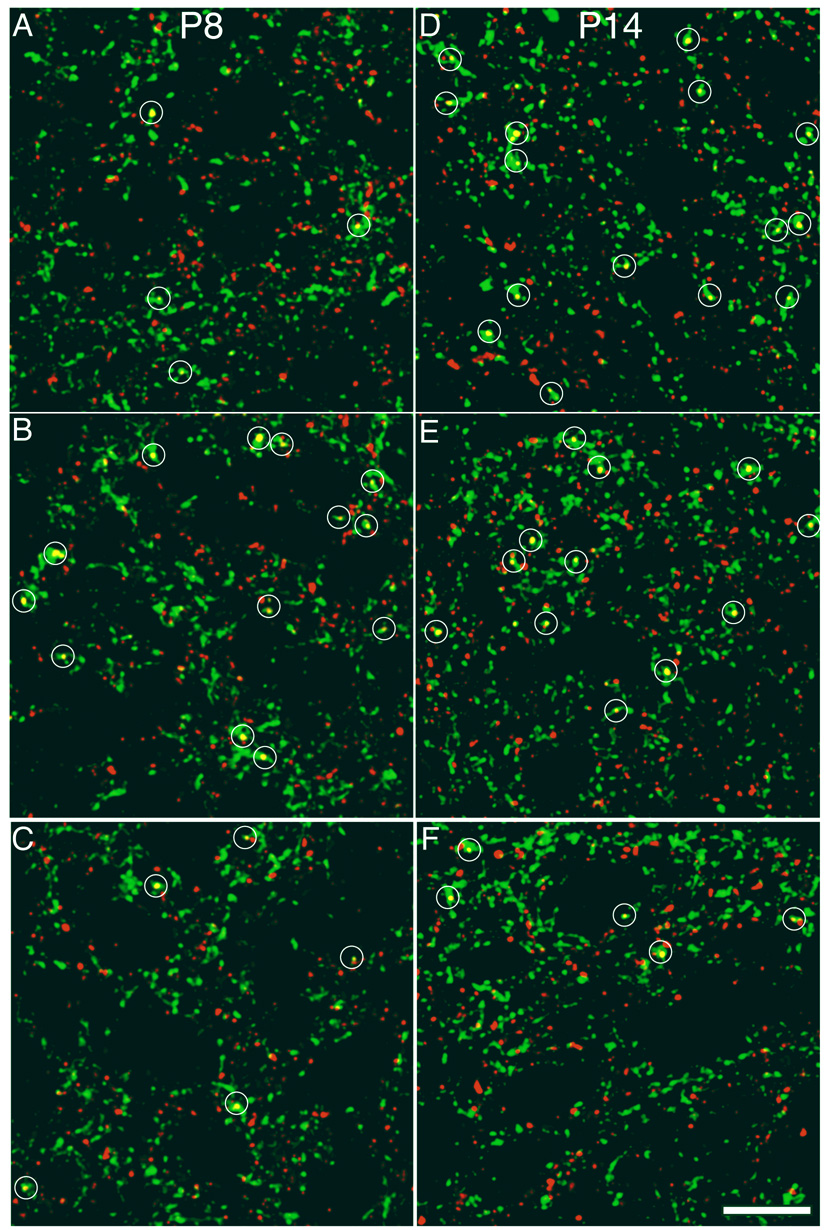
Figure 4. NMDA receptor activity regulates synaptic density on contralateral retinal axons in an age dependent manner.
Sample confocal micrographs of the SGS from various ages and treatment groups that show contralateral retinal axons (green) and synaptophysin label (red). Regions of overlap (yellow) that met the criteria for synapses are marked by a white circle. Drug treatment was provided by the slow release plastic Elvax in which an NMDAR antagonist (D-AP5), an agonist (NMDA) or an appropriate control (L-AP5 or water) was infused. Pups were killed during the period of retinotopic map refinement (P8) or after eye opening and map-refinement (P14). The panels are from the following treatment groups. A. P8 Control, four synapses; B. P8 NMDAR antagonist-treated, thirteen synapses; C. P8 NMDAR agonist-treated, four synapses; D. P14 Control, fifteen synapses; E. P14 NMDAR antagonist-treated, twelve synapses; F. P14 NMDAR agonist-treated, five synapses. Scale bar 10 µm.