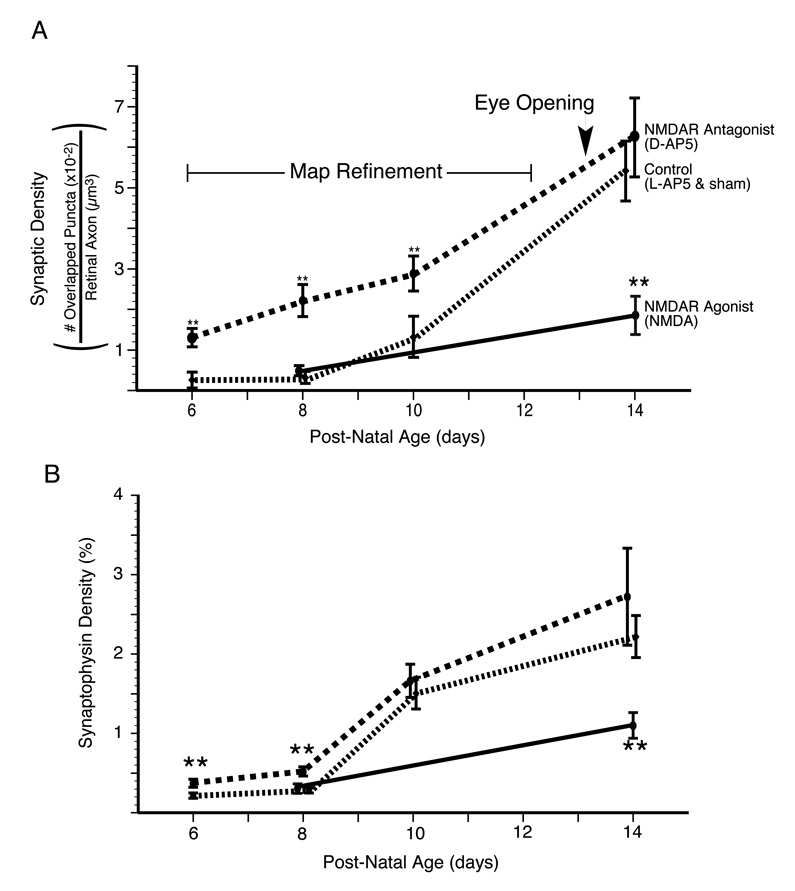
Figure 5. NMDA receptor activity suppresses synapse formation during the period of retinocollicular map refinement.
The average and standard error of RGC axon synaptic density for two experimental treatments--(1)NMDAR antagonist (D-AP5) treated (red) and (2) NMDAR agonist-treated (green)--and (3) the grouped controls are plotted. The control littermates from each of these experiments (L-AP5 and sham Elvax, respectively) have been grouped. NMDAR blockade increased synaptic density when animals were killed on P6, P8 or P10 but not P14. Conversely, agonist-treatment, known to functionally depress synapses, reduced densities at P14 but not P8. That NMDAR blockade increases synaptic density during the period of topographic refinement suggests that at this time the receptor is functioning to actively reduce synapse number on RGC axons. B. A second analysis of the same images to determine total density of synaptophysin staining within the retinal axons. This analysis shows our results are not dependent on the minimum size criterion for puncta, but that total synaptophysin density is regulated in a manner similar to synaptic density. Double asterisk indicates significant difference (p<0.01) from the age-matched, treatment-specific control group.