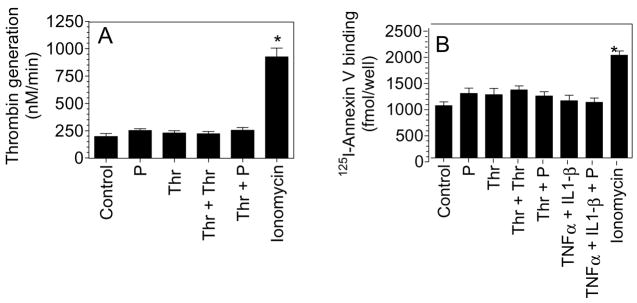
Fig. 5.
Plasmin treatment does not lead to increased anionic phospholipids at the cell surface. HUVEC monolayers were stimulated with plasmin or thrombin for 6 h or first stimulated with thrombin or TNFα + IL1-β for 6 h and then treated with plasmin for 30 min. As a positive control, HUVEC were treated with calcium ionomycin (10 μM) for 3 min. (A) Cell surface prothrombinase activity was measured by adding FXa (1 nM), FVa (10 nM) and prothrombin (1.4 μM) and measuring the rate of thrombin generation. (B) Stimulated cells were incubated with 125I-Annexin V (20 nM) for 2 h at 4°C, and at the end of 2 h surface binding of radioligand was determined. The concentration of plasmin, thrombin, TNFα and IL1-β used in this experiment was same as denoted for other figures. * denotes significantly differs from the control vehicle-treated cells (p < 0.05). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n=3 to 5 experiments).