Fig. 2. Exogenous triple mutant constitutive-active (CA) FoxO3a expression causally prevents non-amyloidogenic processing of APP coincidental with increased Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 contents in the conditioned medium of cortico-hippocampal Tg2576 neurons.
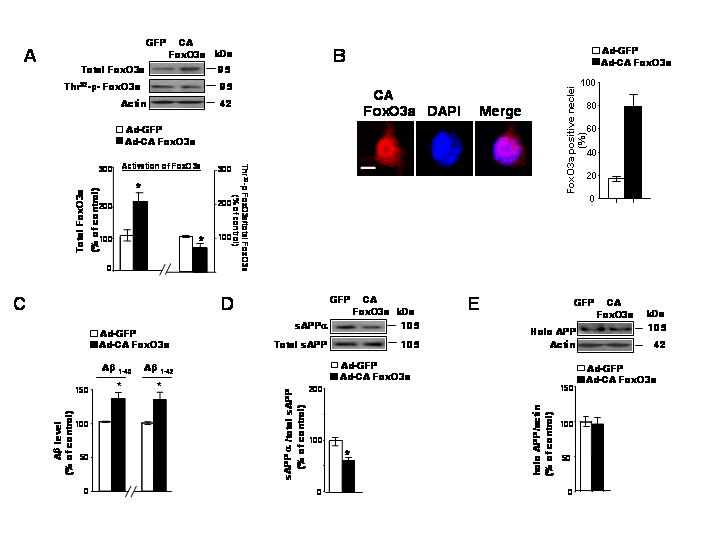
(A) Tg2576 neuron cultures were infected with adenovirus expressing GFP or CA FoxO3a for 48h. Resulting cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis of adenovirus mediated-FoxO3a expression and Thr32-p-FoxO3a content using anti-FoxO3a antibody and Thr32-p-FoxO3a antibody, respectively. (B) Subconfluent Tg2576 neurons were cultures on Lab-Tek chamber slides and infected with CA FoxO3a adenovirus for 24 h. The cells were then fixed and immunofluorescence staining for FoxO3a (a) using anit-FKHRL-1 antibody, which is visualized using Texas Red. In (B) nuclei were identified using DAPI staining (blue). Scale bar: 20μM. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for three separate experiments (n= 100 cells per experiment). (C) Adenovirus-mediated over-expression of CA FoxO3a in Tg2576 neuron cultures lead to increased contents of Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 released into the culture media. Aβ contents were assessed by ELISA 48 hr post-infection (10 MOI). (D) Assessment of changes in sAPPa concentration and (E) full-length APP (expressed as % of total sAPP and actin immunoreactivity, respectively) in response to adenoviral CA FoxO3a expression in Tg2576 neurons. Results are expressed as a % of control (adeno-GFP) infection; values represent means ± SEM of determinations made in three separate culture preparations; n=3 per culture preparation. *p<0.05 versus control group.
