Fig. 4.
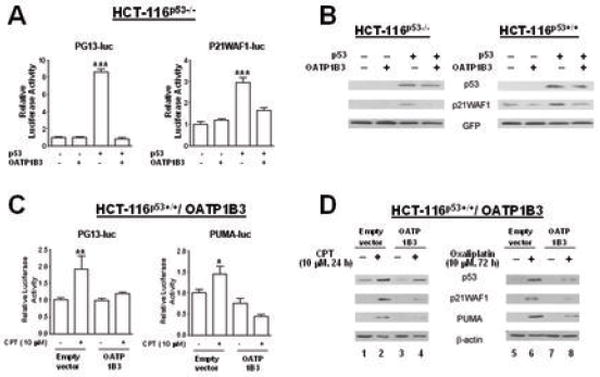
Co-expression of OATP1B3 affects p53 transcriptional activity. A: The results from the p53-responsive PG13-luc and P21WAF1-luc reporter assays in HCT-116p53-/- cells demonstrate that OATP1B3 expression causes a decrease in the transcriptional activity of exogenous p53. B: The results from immunoblotting analysis indicate that co-transfection of OATP1B3 with p53 results in decreases in the protein level of P21WAF1, a p53 downstream target in HCT-116p53-/- and HCT-116p53+/+ cells. C: The results from the p53-responsive PG13-luc or PUMA-luc reporter assay in HCT-116p53+/+ cells stably overexpressing OATP1B3 or empty vector show that CPT treatment increased reporter activity in the empty vector controls, but not in cells overexpressing OATP1B3. D: HCT-116p53+/+ cells stably overexpressing OATP1B3 or the empty vector showed induction of p53 protein upon chemotherapy treatment. However, the levels of the p53 downstream targets, P21WAF1 and PUMA were substantially lower or undetectable in chemotherapy-treated OATP1B3 overexpressing cells compared to chemotherapy-treated empty vector control cells (lanes 2 vs 4 for CPT treatment, 6 vs 8 for oxaliplatin treatment). (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001, different from the rest, ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey test)
